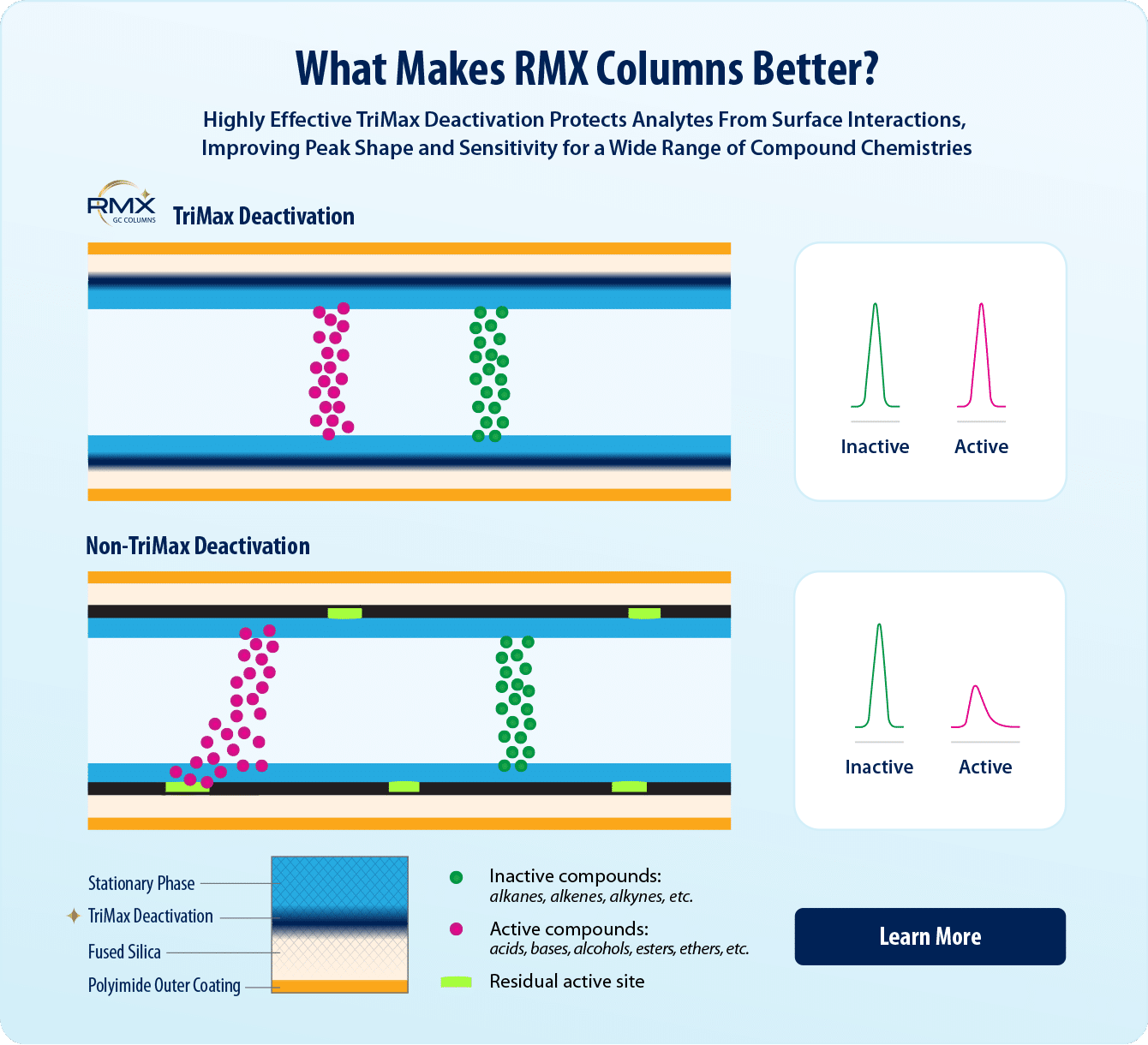
Key Highlights
- Groundbreaking TriMax deactivation creates a robust and exceptionally inert sample flow path for 150 compounds, including acids, bases, and neutrals.
- Maximum inertness improves peak shape for a wide range of semivolatiles, allowing method consolidation and picogram-level sensitivity.
- More flexibility—implement our method for 150 semivolatiles or optimize conditions for your own analyte list in seconds with Restek’s free EZGC chromatogram modeler.

Semivolatiles analysis is a cornerstone application in environmental testing laboratories around the world. Because semivolatiles vary extensively in compound chemistry and reactivity, they are often analyzed on different columns, which means valuable productivity gains can be made if methods can be consolidated onto a single column. However, successful method consolidation hinges on the effectiveness of the GC column deactivation, and traditional deactivations tend to work well for some compound classes but not for others. Restek has developed a next-generation TriMax deactivation technology that is applied to all RMX columns and has been proven to be broadly effective, outperforming even premium competitor columns [1].
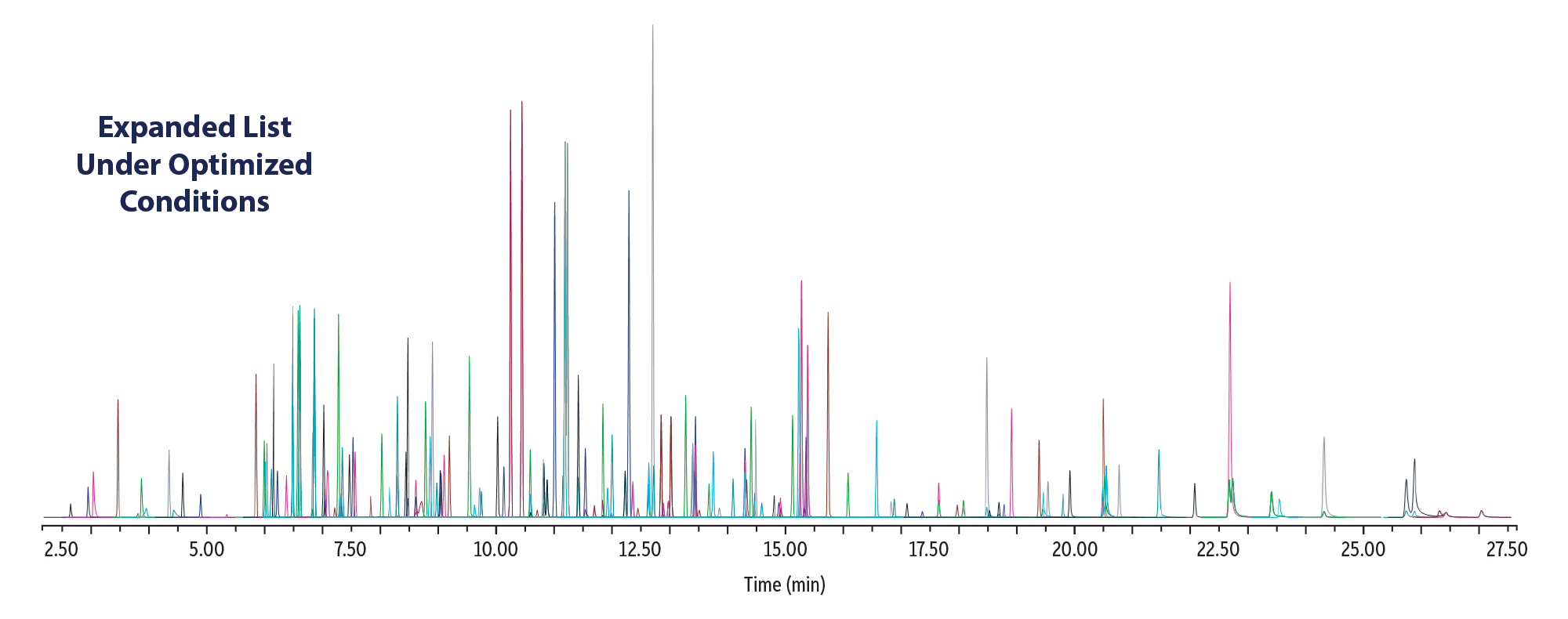
A recent study showed that RMX-5Sil MS columns produced more symmetrical peak shapes across a wider range of semivolatile classes, which resulted in more compounds meeting data requirements for linearity and recovery [2]. The current application expands on that foundational work by optimizing analytical conditions and extending the target compound list to 150 commonly analyzed semivolatiles, including internal standards and surrogates (Figure 1). As shown in Figure 2, excellent chromatographic results were obtained at trace levels (0.1-10 pg on-column) for semivolatiles across all compound classes, including reactive acidic (pentachlorophenol, benzoic acid) and basic (pyridine, benzidine) compounds that often have data quality requirements for system suitability. In addition, the RMX-5Sil MS column adequately separated neutral polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons that are difficult to resolve (benzo[b] and [k]fluoroanthene).
While this consolidated trace-level semivolatiles method demonstrates the effectiveness of an RMX-5Sil MS column across an extensive list of 150 frequently analyzed semivolatiles (cat.# 31907), labs can further adapt it to their needs using free EZGC chromatogram modeling software to instantly create optimized methods for their own specific analyte lists and preferred column dimensions.
Figure 1: Expanded Trace-Level Semivolatiles Method for 150 Semivolatiles, Surrogates, and Internal Standards at 100 ppb (10 pg On-Column)
GC_EV1527
Peaks
| Peaks | tR (min) | Conc. (ng/mL) | Mass 1 | Product 1 | Collision energy 1 | Mass 2 | Product 2 | Collision energy 2 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 1,4-Dioxane | 2.71 | 10 | 58 | 28 | 6 | 88 | 28 | 14 |
| 2. | N-Nitrosodimethylamine | 3.02 | 10 | 74 | 44 | 6 | 74 | 42 | 16 |
| 3. | Pyridine | 3.08 | 10 | 79 | 52 | 12 | 52 | 26 | 18 |
| 4. | Ethyl methacrylate | 3.51 | 10 | 69 | 41 | 6 | 99 | 43 | 14 |
| 5. | 2-Picoline | 3.91 | 10 | 93 | 66 | 12 | 93 | 65 | 18 |
| 6. | N-Nitrosomethylethylamine | 4 | 10 | 88 | 71 | 6 | 88 | 42 | 16 |
| 7. | Methyl methanesulfonate | 4.39 | 10 | 80 | 65 | 8 | 80 | 48 | 28 |
| 8. | Acrylamine | 4.44 | 10 | 71 | 55 | 6 | 71 | 44 | 22 |
| 9. | 2-Fluorophenol | 4.62 | 10 | 112 | 92 | 6 | 92 | 63 | 14 |
| 10. | N-Nitrosodiethylamine | 4.94 | 10 | 102 | 85 | 6 | 102 | 44 | 10 |
| 11. | Ethyl methanesulfonate | 5.38 | 10 | 109 | 45 | 10 | 109 | 79 | 6 |
| 12. | Benzaldehyde | 5.88 | 10 | 105 | 77 | 10 | 105 | 51 | 26 |
| 13. | Phenol-d6 | 6.02 | 10 | 99 | 71 | 8 | 71 | 42 | 16 |
| 14. | Phenol | 6.04 | 10 | 94 | 66 | 10 | 94 | 39 | 30 |
| 15. | Aniline | 6.07 | 10 | 93 | 66 | 10 | 93 | 65 | 20 |
| 16. | Pentachloroethane | 6.14 | 10 | 167 | 132 | 14 | 167 | 95 | 32 |
| 17. | bis-(2-Chloroethyl)ether | 6.18 | 10 | 93 | 63 | 6 | 63 | 27 | 10 |
| 18. | 2-Chlorophenol | 6.25 | 10 | 128 | 64 | 14 | 128 | 63 | 24 |
| 19. | Decane | 6.4 | 10 | 85 | 43 | 6 | 71 | 43 | 6 |
| 20. | 1,3-Dichlorobenzene | 6.51 | 10 | 146 | 111 | 14 | 146 | 75 | 24 |
| 21. | 1,4-Dichlorobenzene-d4 | 6.61 | 10 | 150 | 115 | 14 | 150 | 76 | 38 |
| 22. | 1,4-Dichlorobenzene | 6.63 | 10 | 146 | 111 | 14 | 146 | 75 | 24 |
| 23. | Benzyl alcohol | 6.85 | 10 | 108 | 79 | 12 | 108 | 77 | 24 |
| 24. | 1,2-Dichlorobenzene | 6.89 | 10 | 146 | 111 | 12 | 111 | 50 | 36 |
| 25. | Indene | 7.05 | 10 | 115 | 89 | 16 | 116 | 89 | 28 |
| 26. | 2-Methylphenol | 7.06 | 10 | 108 | 80 | 8 | 108 | 77 | 24 |
| 27. | 2,2′-oxybis(1-chloropropane) | 7.11 | 10 | 121 | 45 | 6 | 77 | 51 | 14 |
| 28. | N-Nitrosopyrrolidine | 7.28 | 10 | 100 | 43 | 8 | 100 | 55 | 6 |
| 29. | Acetophenone | 7.31 | 10 | 105 | 77 | 12 | 105 | 51 | 26 |
| 30. | 3- and 4-Methylphenol | 7.33 | 10 | 70 | 43 | 6 | 107 | 77 | 26 |
| 31. | N-Nitrosomorpholine | 7.331 | 10 | 116 | 86 | 6 | 116 | 56 | 10 |
| 32. | o-Toluidine | 7.37 | 10 | 106 | 79 | 8 | 107 | 77 | 26 |
| 33. | Hexachloroethane | 7.49 | 10 | 201 | 166 | 12 | 201 | 131 | 30 |
| 34. | Nitrobenzene-d5 | 7.57 | 10 | 128 | 82 | 12 | 82 | 54 | 12 |
| 35. | Nitrobenzene | 7.62 | 10 | 123 | 77 | 10 | 123 | 51 | 30 |
| 36. | N-Nitrosopiperidine | 7.88 | 10 | 114 | 84 | 6 | 114 | 97 | 6 |
| 37. | Isophorone | 8.05 | 10 | 138 | 82 | 8 | 82 | 54 | 6 |
| 38. | 2-Nitrophenol | 8.19 | 10 | 139 | 109 | 8 | 139 | 81 | 12 |
| 39. | Benzoic acid | 8.31 | 10 | 122 | 77 | 20 | 105 | 77 | 10 |
| 40. | 2,4-Dimethylphenol | 8.32 | 10 | 122 | 107 | 12 | 122 | 77 | 26 |
| 41. | O,O,O-Triethyl phosphorothioate | 8.46 | 10 | 121 | 65 | 10 | 198 | 114 | 12 |
| 42. | Bis(2-chloroethoxy)methane | 8.5 | 10 | 63 | 27 | 12 | 93 | 63 | 6 |
| 43. | 2,4-Dichlorophenol | 8.64 | 10 | 98 | 63 | 8 | 162 | 98 | 12 |
| 44. | Phentermine | 8.78 | 10 | 58 | 42 | 22 | 134 | 91 | 20 |
| 45. | 1,2,4-Trichlorobenzene | 8.8 | 10 | 180 | 145 | 12 | 180 | 109 | 24 |
| 46. | Naphthalene-d8 | 8.89 | 10 | 136 | 134 | 14 | 136 | 84 | 20 |
| 47. | Naphthalene | 8.92 | 10 | 128 | 102 | 16 | 129 | 103 | 14 |
| 48. | α-Terpineol | 9 | 10 | 136 | 121 | 8 | 136 | 93 | 10 |
| 49. | 4-Chloroaniline | 9.06 | 10 | 127 | 100 | 10 | 127 | 65 | 20 |
| 50. | 2,6-Dichlorophenol | 9.07 | 10 | 162 | 126 | 8 | 164 | 63 | 26 |
| 51. | Hexachloropropene | 9.12 | 10 | 213 | 119 | 18 | 215 | 119 | 18 |
| 52. | Hexachlorobutadiene | 9.21 | 10 | 225 | 190 | 14 | 260 | 190 | 26 |
| 53. | Quinoline | 9.56 | 10 | 129 | 102 | 16 | 129 | 76 | 26 |
| 54. | Caprolactam | 9.65 | 10 | 113 | 85 | 6 | 113 | 56 | 10 |
| 55. | 1,4-Phenylenediamine | 9.73 | 10 | 108 | 81 | 10 | 108 | 80 | 20 |
| 56. | N-Nitrosodibutylamine | 9.76 | 10 | 116 | 99 | 6 | 116 | 74 | 8 |
| 57. | 4-Chloro-3-methylphenol | 10.05 | 10 | 142 | 107 | 12 | 142 | 77 | 26 |
| 58. | Isosafrole I | 10.14 | 10 | 131 | 103 | 8 | 162 | 104 | 12 |
| 59. | 2-Methylnaphthalene | 10.27 | 10 | 141 | 115 | 16 | 141 | 89 | 30 |
| 60. | 1-Methylnaphthalene | 10.46 | 10 | 141 | 115 | 16 | 141 | 89 | 30 |
| 61. | 1,2,4,5-Tetrachlorobenzene | 10.61 | 10 | 216 | 181 | 14 | 216 | 108 | 36 |
| 62. | Hexachloropentadiene | 10.62 | 10 | 272 | 237 | 12 | 237 | 143 | 22 |
| 63. | 2,3-Dichloroaniline | 10.83 | 10 | 161 | 90 | 16 | 163 | 90 | 18 |
| 64. | 2,4,6-Trichlorophenol | 10.85 | 10 | 132 | 97 | 10 | 196 | 97 | 24 |
| 65. | 2,4,5-Trichlorophenol | 10.95 | 10 | 132 | 97 | 10 | 196 | 97 | 24 |
| 66. | 2-Fluorobiphenyl | 11.03 | 10 | 172 | 171 | 12 | 172 | 170 | 22 |
| 67. | 2-Chloronaphthalene | 11.15 | 10 | 162 | 127 | 16 | 162 | 77 | 30 |
| 68. | Isosafrole II | 11.17 | 10 | 131 | 103 | 10 | 162 | 104 | 12 |
| 69. | Safrole | 11.2 | 10 | 162 | 127 | 16 | 131 | 103 | 10 |
| 70. | Biphenyl | 11.21 | 10 | 154 | 152 | 22 | 153 | 126 | 32 |
| 71. | 1-Chloronaphthalene | 11.25 | 10 | 162 | 127 | 16 | 127 | 77 | 16 |
| 72. | o-Nitroaniline | 11.43 | 10 | 138 | 92 | 12 | 138 | 65 | 22 |
| 73. | Diphenyl ether | 11.43 | 10 | 170 | 142 | 10 | 141 | 115 | 14 |
| 74. | 1,4-Naphthoquinone | 11.57 | 10 | 158 | 130 | 8 | 158 | 102 | 14 |
| 75. | 1,2-Dinitrobenzene | 11.86 | 10 | 122 | 75 | 12 | 168 | 75 | 20 |
| 76. | 1,3-Dinitrobenzene | 11.87 | 10 | 168 | 75 | 20 | 76 | 50 | 10 |
| 77. | Diphenyl phthalate | 11.87 | 10 | 163 | 133 | 8 | 163 | 77 | 20 |
| 78. | 1,6-Dinitrotoluene | 11.95 | 10 | 165 | 148 | 8 | 165 | 63 | 20 |
| 79. | 1,4-Dinitrobenzene | 12.01 | 10 | 168 | 51 | 14 | 76 | 63 | 6 |
| 80. | Acenaphthylene | 12.02 | 10 | 152 | 126 | 24 | 152 | 76 | 36 |
| 81. | 3-Nitroaniline | 12.25 | 10 | 92 | 65 | 8 | 138 | 65 | 20 |
| 82. | Acenaphthene-d10 | 12.32 | 10 | 164 | 162 | 14 | 164 | 160 | 32 |
| 83. | Acenaphthene | 12.37 | 10 | 153 | 126 | 36 | 153 | 77 | 38 |
| 84. | 2,4-Dinitrophenol | 12.46 | 10 | 184 | 154 | 6 | 184 | 107 | 10 |
| 85. | 4-Nitrophenol | 12.65 | 10 | 139 | 109 | 6 | 139 | 81 | 14 |
| 86. | Pentachlorobenzene | 12.66 | 10 | 250 | 215 | 16 | 250 | 142 | 38 |
| 87. | Dibenzofuran | 12.73 | 10 | 168 | 139 | 22 | 139 | 63 | 30 |
| 88. | 2,4-Dinitrotoluene | 12.74 | 10 | 165 | 119 | 6 | 165 | 63 | 22 |
| 89. | 1-Naphthylamine | 12.88 | 10 | 143 | 116 | 10 | 143 | 115 | 22 |
| 90. | 2,3,5,6-Tetrachlorophenol | 12.91 | 10 | 232 | 168 | 12 | 234 | 133 | 26 |
| 91. | 2,3,4,6-Tetrachlorophenol | 13 | 10 | 232 | 168 | 12 | 234 | 131 | 24 |
| 92. | 2-Naphthylamine | 13.03 | 10 | 143 | 116 | 10 | 143 | 115 | 22 |
| 93. | Diethyl Phthalate | 13.3 | 10 | 177 | 149 | 8 | 149 | 65 | 20 |
| 94. | Hexadecane | 13.41 | 10 | 85 | 43 | 6 | 99 | 41 | 14 |
| 95. | Fluorene | 13.41 | 10 | 165 | 139 | 26 | 167 | 166 | 14 |
| 96. | Zinophos | 13.45 | 10 | 143 | 79 | 10 | 107 | 52 | 20 |
| 97. | 5-Nitro-o-toluidine | 13.45 | 10 | 152 | 106 | 10 | 152 | 77 | 24 |
| 98. | 4-Nitroaniline | 13.46 | 10 | 138 | 108 | 8 | 138 | 80 | 18 |
| 99. | 4-Chlorophenyl phenyl ether | 13.46 | 10 | 204 | 77 | 22 | 141 | 115 | 14 |
| 100. | 4,6-Dinitro-2-methylphenol | 13.54 | 10 | 198 | 168 | 6 | 198 | 121 | 10 |
| 101. | Diphenylamine | 13.7 | 10 | 169 | 66 | 22 | 169 | 77 | 30 |
| 102. | Azobenzene | 13.76 | 10 | 182 | 105 | 6 | 182 | 77 | 12 |
| 103. | 2,4,6-Tribromophenol | 13.88 | 10 | 330 | 222 | 20 | 332 | 143 | 34 |
| 104. | Sulfotepp | 14.1 | 10 | 202 | 146 | 10 | 322 | 146 | 24 |
| 105. | 1,3,5-Trinitrobenzene | 14.23 | 10 | 213 | 167 | 8 | 213 | 74 | 38 |
| 106. | Diallate 1 | 14.31 | 10 | 86 | 43 | 6 | 234 | 150 | 16 |
| 107. | Phorate | 14.32 | 10 | 75 | 47 | 8 | 121 | 47 | 26 |
| 108. | Phenacetin | 14.35 | 10 | 179 | 137 | 8 | 179 | 109 | 14 |
| 109. | 4-Bromophenyl phenyl ether | 14.41 | 10 | 248 | 141 | 14 | 141 | 115 | 12 |
| 110. | Diallate 2 | 14.48 | 10 | 234 | 150 | 16 | 86 | 43 | 6 |
| 111. | Hexachlorobenzene | 14.5 | 10 | 284 | 249 | 14 | 288 | 216 | 26 |
| 112. | Dimethoate | 14.6 | 10 | 93 | 63 | 8 | 125 | 47 | 14 |
| 113. | Atrazine | 14.82 | 10 | 200 | 122 | 8 | 215 | 200 | 8 |
| 114. | Pentachlorophenol | 14.9 | 10 | 266 | 167 | 22 | 270 | 169 | 22 |
| 115. | 4-Aminobiphenyl | 14.93 | 10 | 168 | 141 | 8 | 168 | 167 | 10 |
| 116. | Pentachloronitrobenzene | 14.93 | 10 | 295 | 265 | 8 | 237 | 143 | 20 |
| 117. | Propyzamide | 15.13 | 10 | 173 | 145 | 14 | 254 | 191 | 16 |
| 118. | Phenanthrene-d10 | 15.24 | 10 | 188 | 160 | 20 | 184 | 154 | 32 |
| 119. | Octadecane | 15.27 | 10 | 85 | 43 | 6 | 99 | 41 | 14 |
| 120. | Phenanthrene | 15.29 | 10 | 178 | 152 | 18 | 178 | 151 | 32 |
| 121. | Dinoseb | 15.34 | 10 | 163 | 116 | 14 | 240 | 117 | 24 |
| 122. | Disulfoton | 15.36 | 10 | 88 | 60 | 6 | 97 | 65 | 16 |
| 123. | Anthracene | 15.39 | 10 | 178 | 152 | 18 | 178 | 151 | 32 |
| 124. | Carbazole | 15.741 | 10 | 167 | 166 | 12 | 167 | 139 | 24 |
| 125. | Methyl Parathion | 16.08 | 10 | 263 | 109 | 10 | 263 | 79 | 24 |
| 126. | di-n-Butyl phthalate | 16.58 | 10 | 149 | 121 | 12 | 149 | 65 | 20 |
| 127. | 4-Nitroquinoline-N-oxide | 16.83 | 10 | 190 | 160 | 8 | 101 | 75 | 10 |
| 128. | Ethyl Parathion | 16.89 | 10 | 109 | 81 | 10 | 291 | 81 | 26 |
| 129. | Methapyrilene | 17.1 | 10 | 97 | 53 | 16 | 190 | 97 | 14 |
| 130. | Isodrin | 17.36 | 10 | 261 | 226 | 16 | 261 | 191 | 28 |
| 131. | Fluoranthene | 17.65 | 10 | 202 | 176 | 26 | 184 | 156 | 18 |
| 132. | Fluoranthene | 17.65 | 10 | 202 | 152 | 30 | 200 | 174 | 22 |
| 133. | Benzidine | 17.99 | 10 | 184 | 166 | 16 | 200 | 149 | 34 |
| 134. | Pyrene | 18.08 | 10 | 200 | 150 | 26 | 212 | 208 | 36 |
| 135. | p-Terphenyl-d14 | 18.5 | 10 | 244 | 242 | 14 | 244 | 240 | 22 |
| 136. | Aramite 1 | 18.55 | 10 | 319 | 185 | 6 | 175 | 107 | 14 |
| 137. | Aramite 2 | 18.7 | 10 | 185 | 63 | 12 | 319 | 185 | 6 |
| 138. | p-Dimethylaminoazobenzene | 18.79 | 10 | 225 | 148 | 6 | 120 | 77 | 16 |
| 139. | Chlorobenzilate | 18.93 | 10 | 251 | 139 | 12 | 251 | 111 | 30 |
| 140. | Famfur | 19.4 | 10 | 218 | 109 | 14 | 125 | 79 | 6 |
| 141. | 3,3′-Dimethylbenzidine | 19.46 | 10 | 211 | 196 | 8 | 211 | 195 | 16 |
| 142. | Kepone | 19.47 | 10 | 272 | 237 | 12 | 237 | 143 | 22 |
| 143. | Benzyl butyl phthalate | 19.56 | 10 | 206 | 149 | 8 | 149 | 121 | 10 |
| 144. | Bis(2-ethylhexyl) adipate | 19.81 | 10 | 129 | 55 | 14 | 129 | 83 | 8 |
| 145. | 2-Acetylaminofluorene | 19.93 | 10 | 223 | 181 | 10 | 181 | 152 | 34 |
| 146. | Benz[a]anthracene | 20.5 | 10 | 228 | 202 | 22 | 226 | 200 | 28 |
| 147. | Chrysene-d12 | 20.51 | 10 | 240 | 238 | 14 | 240 | 236 | 30 |
| 148. | 3,3′-Dichlorobenzidine | 20.51 | 10 | 252 | 181 | 22 | 252 | 182 | 20 |
| 149. | 4,4′-Methylenebis(2-chloroaniline) | 20.53 | 10 | 231 | 195 | 16 | 266 | 231 | 12 |
| 150. | Chrysene | 20.56 | 10 | 228 | 202 | 22 | 228 | 201 | 36 |
| 151. | Bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate | 20.78 | 10 | 167 | 149 | 8 | 149 | 121 | 14 |
| 152. | 6-Methylchrysene | 21.46 | 10 | 242 | 226 | 28 | 239 | 213 | 26 |
| 153. | Di-n-octyl phthalate | 22.08 | 10 | 149 | 121 | 12 | 149 | 93 | 16 |
| 154. | Benzo[b]fluoranthene | 22.68 | 10 | 252 | 226 | 22 | 250 | 224 | 24 |
| 155. | 7,12-Dimethylbenz[a]anthracene | 22.69 | 10 | 256 | 241 | 12 | 241 | 226 | 14 |
| 156. | Benzo[k]fluoranthene | 22.74 | 10 | 252 | 226 | 22 | 250 | 224 | 24 |
| 157. | Benzo[a]pyrene | 23.41 | 10 | 252 | 226 | 22 | 250 | 224 | 26 |
| 158. | Perylene-d12 | 23.55 | 10 | 264 | 262 | 20 | 264 | 260 | 34 |
| 159. | 3-Methylcholanthrene | 24.32 | 10 | 268 | 253 | 14 | 252 | 226 | 22 |
| 160. | Dibenz(a,h)acridine | 25.8 | 10 | 279 | 252 | 34 | 278 | 250 | 24 |
| 161. | Dibenz[a,j]acridine | 25.88 | 10 | 279 | 277 | 30 | 278 | 250 | 26 |
| 162. | Indeno[1,2,3-cd]pyrene | 26.32 | 10 | 138 | 125 | 12 | 276 | 250 | 30 |
| 163. | Dibenz[a,h]anthracene | 26.43 | 10 | 139 | 126 | 8 | 139 | 113 | 14 |
| 164. | Benzo[ghi]perylene | 27.05 | 10 | 138 | 125 | 12 | 138 | 124 | 28 |
Conditions
| Column | RMX-5Sil MS, 30 m, 0.25 mm ID, 0.25 µm (cat.# 17323) |
|---|---|
| Standard/Sample | |
| SVOC MegaMix 150 kit (cat.# 31907) | |
| Revised SV internal standard mix (cat.# 31886) | |
| Base neutral surrogate mix (4/89 SOW) (cat.# 31024) | |
| Acid surrogate mix (4/89 SOW) (cat.# 31025) | |
| Diluent: | Dichloromethane |
| Conc.: | 100 ppb |
| Injection | |
| Inj. Vol.: | 1 µL split (split ratio 10:1) |
| Liner: | Topaz 4.0 mm ID Precision liner w/wool (cat.# 23267) |
| Inj. Temp.: | 280 °C |
| Split Vent Flow Rate: | 12 mL/min |
| Oven | |
| Oven Temp.: | 40 °C (hold 1 min) to 280 °C at 12 °C/min to 310 °C at 3 °C/min (hold 1 min) |
| Carrier Gas | He, constant flow |
| Flow Rate: | 1.2 mL/min @ 40 °C |
| Detector | SRM/MRM |
|---|---|
| Source Temp.: | 330 °C |
| Transfer Line Temp.: | 280 °C |
| Analyzer Type: | Triple Quadrupole |
| Ionization Mode: | EI |
| Collision Gas: | Ar |
| Tune Type: | PFTBA |
| Tune Emission Current: | 70 μA |
| Instrument | Thermo Scientific TSQ 8000 Triple Quadrupole GC-MS |
| Sample Preparation | Standards were combined and diluted to a concentration of 100 ppb. |
Figure 2: Highly inert RMX-5Sil MS columns help you meet data requirements for a wide range of challenging semivolatiles at extremely low levels.

GC_EV1526
Conditions
| Column | RMX-5Sil MS, 30 m, 0.25 mm ID, 0.25 µm (cat.# 17323) |
|---|---|
| Standard/Sample | |
| SVOC MegaMix 150 kit (cat.# 31907) | |
| Revised SV internal standard mix (cat.# 31886) | |
| Base neutral surrogate mix (4/89 SOW) (cat.# 31024) | |
| Acid surrogate mix (4/89 SOW) (cat.# 31025) | |
| Diluent: | Dichloromethane |
| Conc.: | 1, 10, 100 ppb |
| Injection | |
| Inj. Vol.: | 1 µL split (split ratio 10:1) |
| Liner: | Topaz 4.0 mm ID Precision liner w/wool (cat.# 23267) |
| Inj. Temp.: | 280 °C |
| Split Vent Flow Rate: | 12 mL/min |
| Oven | |
| Oven Temp.: | 40 °C (hold 1 min) to 280 °C at 12 °C/min to 310 °C at 3 °C/min (hold 1 min) |
| Carrier Gas | He, constant flow |
| Flow Rate: | 1.2 mL/min @ 40 °C |
| Detector | SRM/MRM |
|---|---|
| Source Temp.: | 330 °C |
| Transfer Line Temp.: | 280 °C |
| Analyzer Type: | Triple Quadrupole |
| Ionization Mode: | EI |
| Collision Gas: | Ar |
| Tune Type: | PFTBA |
| Tune Emission Current: | 70 μA |
| Instrument | Thermo Scientific TSQ 8000 Triple Quadrupole GC-MS |
References
- RMX GC columns brochure, GNBR4923-UNV, Restek Corporation, 2026.
- E. Pack, J. Hoisington, C. English, R. Dhandapani, and C. Myers, Comprehensive trace-level semivolatiles analysis by GC-MS/MS (EPA Method 8270E), Application note, EVAN4919-US, Restek Corporation, 2025.