Abstract
In this method evaluation study, we demonstrated the performance of a fast dilute-and-shoot LC-MS/MS method using a Raptor Biphenyl column for the simultaneous analysis of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), vanillylmandelic acid (VMA), and homovanillic acid (HVA) in human urine. Excellent results were obtained for linearity, accuracy, and precision. With this method, these serotonin and catecholamine metabolites can be measured in human urine with a 5-minute total analysis time. The analytical method is applicable to clinical labs that require a combination of fast analysis times and low-cost sample preparation procedures for 5-HIAA, VMA, and HVA using LC-MS/MS analysis.
Introduction
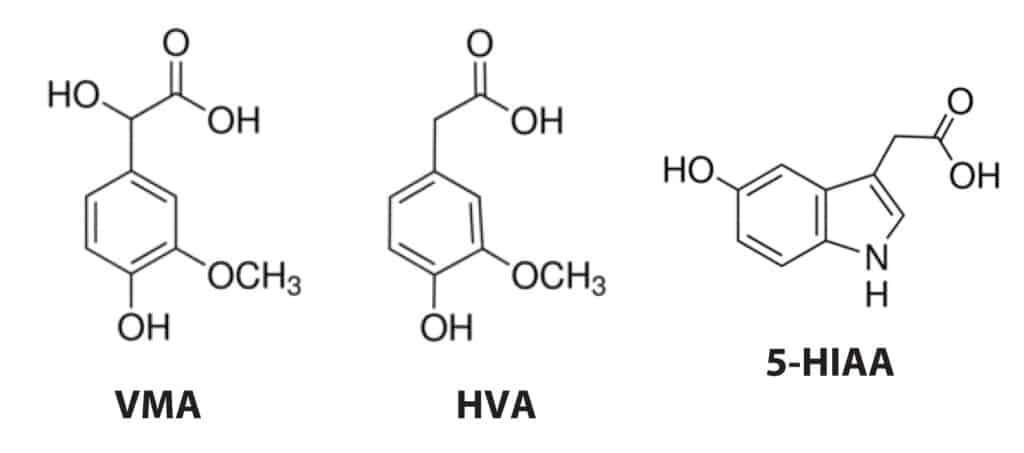
5-Hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), vanillylmandelic acid (VMA), and homovanillic acid (HVA) are the final metabolites of serotonin, epinephrine, and dopamine, respectively (Figure 1). Measurement of these metabolites in urine is used for the diagnosis of carcinoid and neuroendocrine tumors including neuroblastoma, pheochromocytoma, and paraganglioma. Several commercial products are available for the simultaneous measurement of these three analytes in urine. However, these commercial kits all require extensive sample preparation and chromatographic analysis times of up to 16 minutes. The development of a faster and simpler method would greatly reduce the time and cost of this type of clinical test. In this study, we developed a fast dilute-and-shoot method for accurate and specific 5-HIAA, VMA, and HVA LC-MS/MS analysis in urine using a Raptor Biphenyl column. The Raptor Biphenyl column was selected for this work because our initial investigation determined that it offers better peak shape and sensitivity than a C18 column.
Experimental
To evaluate linearity, eight standard solutions (0.2, 0.4, 1.0, 5.0, 10, 25, 50, and 100 µg/mL) were prepared in synthetic human urine (Surine negative urine control, Cerilliant). In addition, two levels of urine control samples (Bio-Rad Lyphochek quantitative urine control, bilevel minipak #375X) were used as QC samples for accuracy and precision analysis. Controls 1 and 2 were described by Bio-Rad Laboratories as normal and abnormal levels, respectively, and had labeled concentration ranges (Table II) for 5-HIAA, VMA, and HVA that were determined by Bio-Rad using a reversed-phase HPLC method.
All prepared standards and samples were diluted 10x by mixing 40 µL of prepared standard or sample in urine with 360 µL of water and 10 µL of internal standard solution (33.3 µg/mL of 5-HIAA-D5, VMA-D3, and HVA-D5 in methanol) in a 0.45 µm Thomson SINGLE StEP PVDF filter vial (Restek, cat.# 25896). Standards and samples were filtered and injected for analysis.
5-HIAA, VMA, and HVA LC analysis was performed on a Shimadzu Nexera XR System coupled with a Sciex API 4000 mass spectrometer. Instrument conditions were as follows and analyte transitions are provided in Table I.
| Analytical column: | Raptor Biphenyl (5 µm, 100 mm x 2.1 mm; cat.# 9309512) | |
| Guard column: | Raptor Biphenyl EXP guard column cartridge (5 µm, 5 mm x 2.1 mm; cat.# 930950252) and EXP direct connect holder (cat.# 25808) | |
| Mobile phase A: | 0.1% Formic acid + 5 mM ammonium formate in water | |
| Mobile phase B: | Methanol | |
| Gradient | Time (min) | %B |
| 0.00 | 15 | |
| 3.00 | 80 | |
| 3.01 | 15 | |
| 5.00 | 15 | |
| Flow rate: | 0.5 mL/min | |
| Injection volume: | 5 µL | |
| Column temp.: | 30 °C | |
| Ion mode: | Negative ESI | |
Table I: Analyte Transitions
| Analyte | CAS# | Precursor Ion | Product Ion Quantifier | Product Ion Qualifier |
| 5-HIAA-D5 | — | 195.1 | 148.0 | — |
| 5-HIAA | 54-16-0 | 190.0 | 145.9 | 144.0 |
| VMA-D3 | — | 200.1 | 139.9 | — |
| VMA | 55-10-7 | 197.0 | 137.9 | 136.9 |
| HVA-D5 | — | 186.1 | 127.0 | — |
| HVA | 306-08-1 | 181.0 | 121.9 | 136.9 |
Results and Discussion
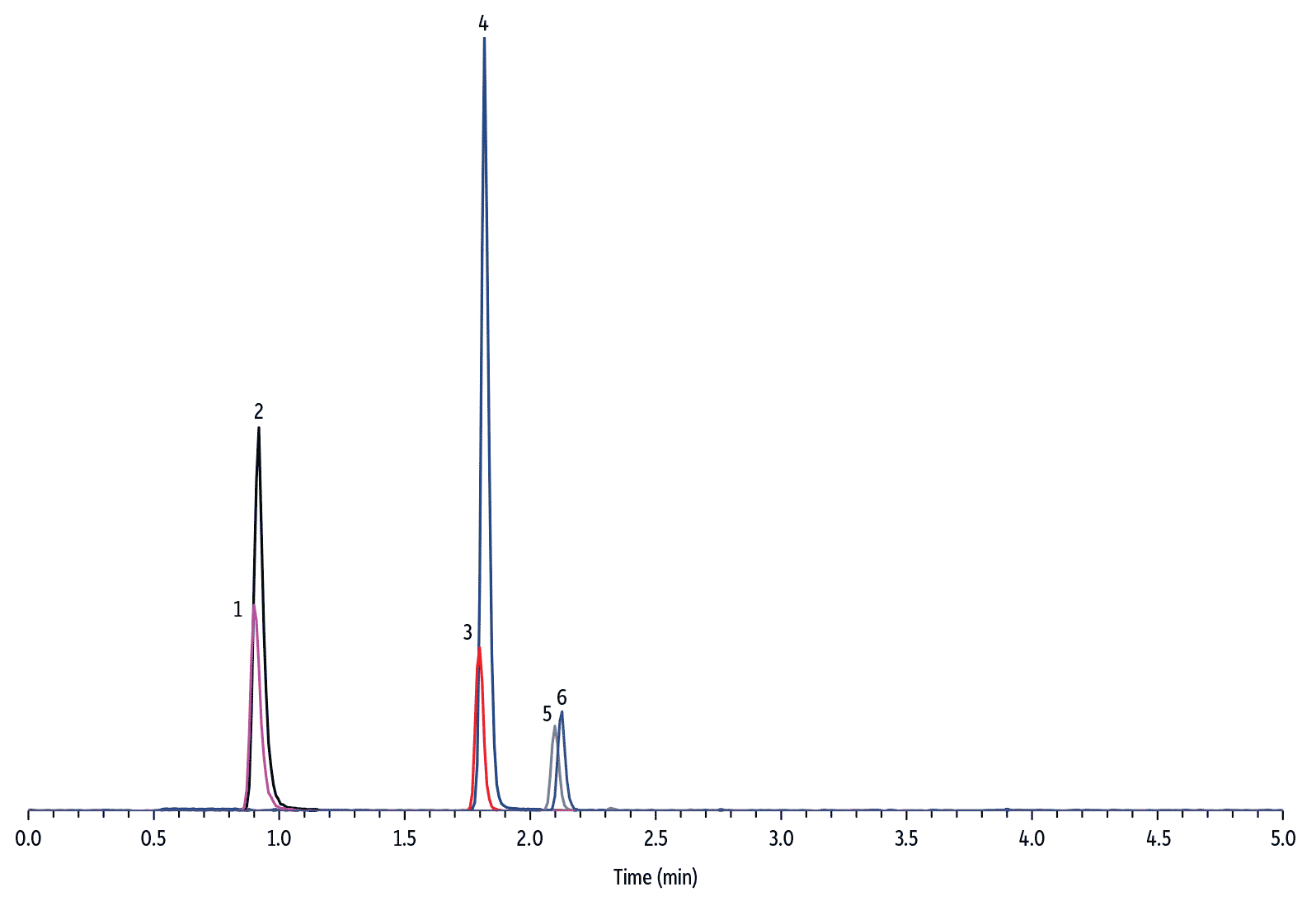
To develop a quantitative dilute-and-shoot method, it is important to ensure chromatographic separation of all matrix interferences from the target analytes. Upon initial method development, it was observed that the response of HVA internal standard suffered from urine matrix suppression and resulted in inaccurate measurement of HVA concentration. To solve this problem, it was necessary to modify the additive type in the mobile phase and select an LC column with the proper phase chemistry. The final method demonstrated that the Raptor Biphenyl column is unique in that it offered excellent chromatographic performance for simultaneous accurate and precise quantification of 5-HIAA, VMA, and HVA in diluted human urine samples (see Figure 3, 4, and 5 for representative chromatograms).
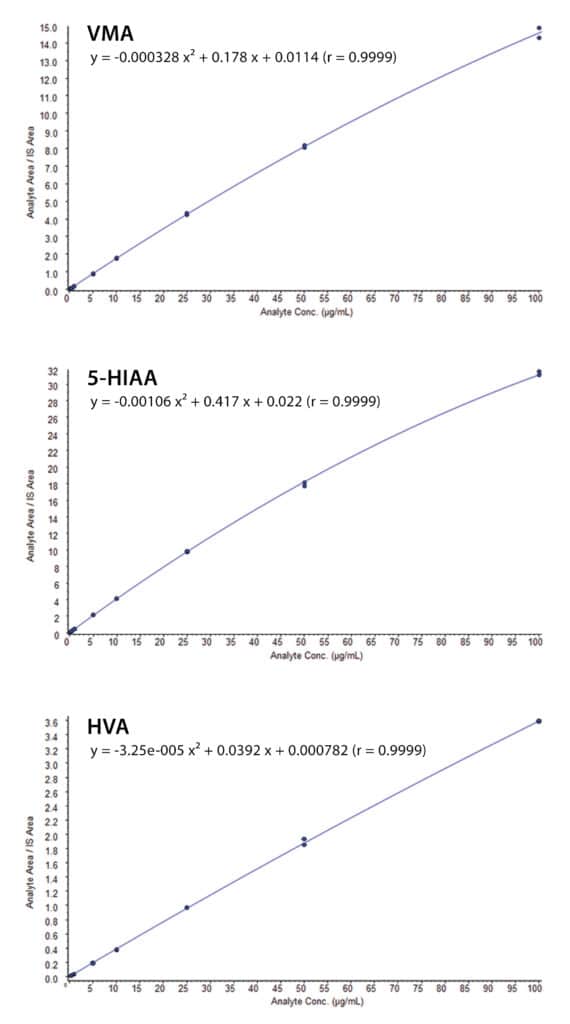
Linear responses were obtained from 0.2–100 µg/mL for 5-HIAA, VMA, and HVA. A 1/x weighted quadratic regression provided the best fit for the standard calibration curves of all three analytes. The deviations were all ≤10% (except for the lowest concentration, which was ≤15%) and the R2 values all were 0.999–1.000 (see examples in Figure 2). As estimated from the signal-to-noise value of the 0.2 µg/mL standard injection, the LODs were 0.03, 0.007, and 0.02 µg/mL for 5-HIAA, VMA, and HVA, respectively.
Three sets of samples were prepared and analyzed to evaluate method accuracy and precision. Method accuracy was demonstrated to be acceptable as the quantitative concentrations fell within the nominal concentration ranges for both the low and high urine control samples (Table II). The %RSD ranged from 0.2–2.8% and 0.2–2.9% for intraday and interday, respectively (data not shown), indicating acceptable method precision.
Table II: Accuracy and Precision of Urine Control Samples
| QC Level 1 (n = 3) | QC Level 2 (n = 3) | |||||
| Analyte | Range (µg/mL)* | Average Conc. (µg/mL) | %RSD | Range (µg/mL)* | Average Conc. (µg/mL) | %RSD |
| 5-HIAA | 2.69–4.49 | 3.59 | 2.2 | 21.6–32.7 | 27.5 | 1.7 |
| VMA | 2.12–3.90 | 3.34 | 1.0 | 10.9–18.2 | 16.3 | 0.2 |
| HVA | 1.33–2.46 | 1.95 | 2.4 | 12.9–18.9 | 17.5 | 2.9 |
*The QC sample concentration ranges were supplied by the vendor.
Conclusion
Commercial kits for the analysis of 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA), vanillylmandelic acid (VMA), and homovanillic acid (HVA), require extensive sample preparation and chromatographic analysis times up to 16 minutes. In contrast, using Restek’s dilute-and-shoot method and a Raptor Biphenyl column, these serotonin and catecholamine metabolites can be measured in a quick 5-minute analysis. This method is applicable to clinical 5-HIAA, VMA, and HVA LC-MS/MS analysis in urine and provides the benefits of both fast analysis times and low-cost sample preparation procedures.
LC_CF0660
Peaks
| Peaks | tR (min) | Conc. (µg/mL) | Precursor Ion | Product Ion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxymandelic acid-D3 (VMA-D3) | 0.90 | 0.83 | 200.1 | 139.9 |
| 2. | Vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) | 0.92 | 1 | 197.0 | 137.9 |
| 3. | 5-Hydroxyindole-4,6,7-D3-3-acetic-D2 acid (5-HIAA-D5) | 1.80 | 0.83 | 195.1 | 148.0 |
| 4. | 5-Hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid (5-HIAA) | 1.82 | 1 | 190.0 | 145.9 |
| 5. | 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl-D3-acetic-D2 acid (HVA-D5) | 2.10 | 0.83 | 186.1 | 127.0 |
| 6. | Homovanillic acid (HVA) | 2.12 | 1 | 181.0 | 121.9 |
Conditions
| Column | Raptor Biphenyl (cat.# 9309512) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions: | 100 mm x 2.1 mm ID | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle Size: | 5 µm | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Pore Size: | 90 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Guard Column: | Raptor Biphenyl guard column cartridge 5 mm, 2.1 mm ID, 5 µm (cat.# 930950252) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Temp.: | 30 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard/Sample | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Diluent: | Water | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Inj. Vol.: | 5 µL | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Mobile Phase | |||||||||||||||||||||
| A: | 0.1% Formic acid, 5 mM ammonium formate in water | ||||||||||||||||||||
| B: | Methanol | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Detector | MS/MS |
|---|---|
| Ion Mode: | ESI- |
| Mode: | MRM |
| Instrument | UHPLC |
| Sample Preparation | The synthetic urine (Surine) was fortified with VMA, HVA, and 5-HIAA to a concentration of 10 μg/mL. A 40 μL aliquot of fortified urine was mixed with 360 μL of water and 10 μL of internal standard solution (33.3 μg/mL in methanol) in a Thomson 0.45 μm PVDF filter vial and injected for analysis after filtration. |
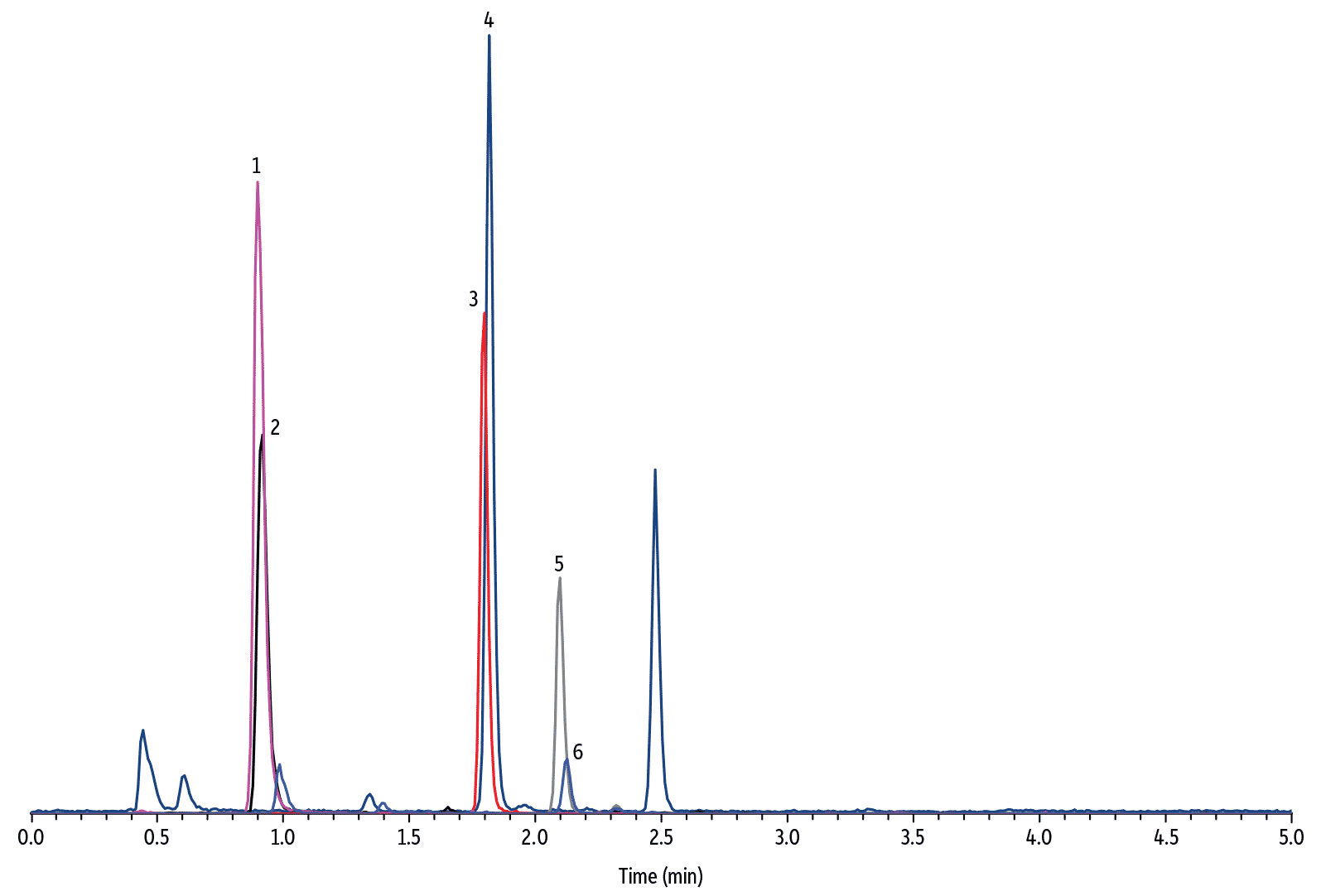
LC_CF0661
Peaks
| Peaks | tR (min) | Conc. (µg/mL) | Precursor Ion | Product Ion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxymandelic acid-D3 (VMA-D3) | 0.90 | 0.83 | 200.1 | 139.9 |
| 2. | Vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) | 0.92 | 2.12–3.90* | 197.0 | 137.9 |
| 3. | 5-Hydroxyindole-4,6,7-D3-3-acetic-D2 acid (5-HIAA-D5) | 1.80 | 0.83 | 195.1 | 148.0 |
| 4. | 5-Hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid (5-HIAA) | 1.82 | 2.69–4.49* | 190.0 | 145.9 |
| 5. | 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl-D3-acetic-D2 acid (HVA-D5) | 2.10 | 0.83 | 186.1 | 127.0 |
| 6. | Homovanillic acid (HVA) | 2.12 | 1.33–2.46* | 181.0 | 121.9 |
Conditions
| Column | Raptor Biphenyl (cat.# 9309512) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions: | 100 mm x 2.1 mm ID | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle Size: | 5 µm | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Pore Size: | 90 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Guard Column: | Raptor Biphenyl guard column cartridge 5 mm, 2.1 mm ID, 5 µm (cat.# 930950252) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Temp.: | 30 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard/Sample | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Diluent: | Water | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Inj. Vol.: | 5 µL | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Mobile Phase | |||||||||||||||||||||
| A: | 0.1% Formic acid, 5 mM ammonium formate in water | ||||||||||||||||||||
| B: | Methanol | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Detector | MS/MS |
|---|---|
| Ion Mode: | ESI- |
| Mode: | MRM |
| Instrument | UHPLC |
| Sample Preparation | The human urine sample is the Bio-Rad Lyphochek quantitative urine control, level 1. A 40 μL aliquot of urine was mixed with 360 μL of water and 10 μL of internal standard solution (33.3 μg/mL in methanol) in a Thomson 0.45 μm PVDF filter vial and injected for analysis after filtration. |
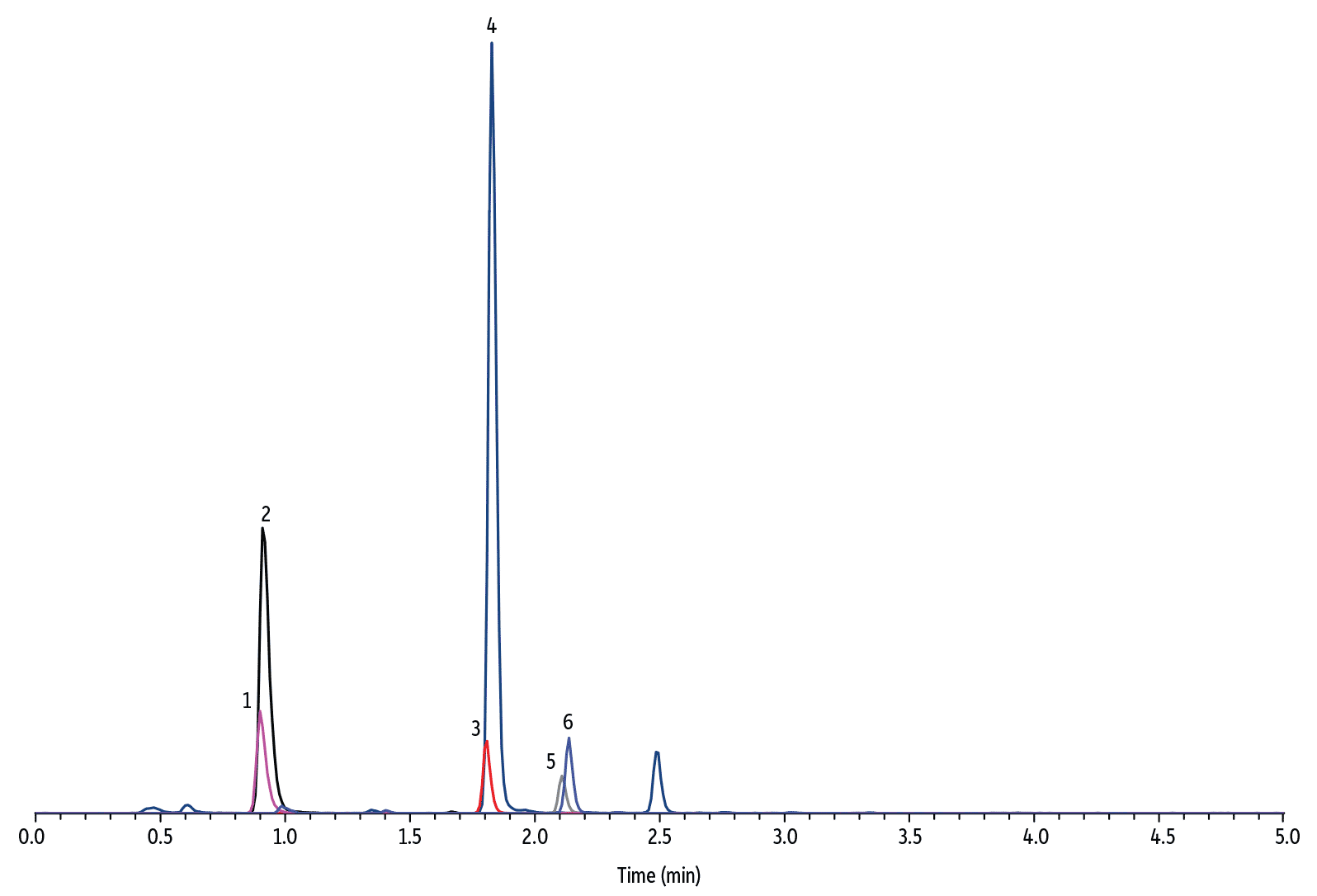
LC_CF0662
Peaks
| Peaks | tR (min) | Conc. (µg/mL) | Precursor Ion | Product Ion | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxymandelic acid-D3 (VMA-D3) | 0.90 | 0.83 | 200.1 | 139.9 |
| 2. | Vanillylmandelic acid (VMA) | 0.91 | 10.9–18.2* | 197.0 | 137.9 |
| 3. | 5-Hydroxyindole-4,6,7-D3-3-acetic-D2 acid (5-HIAA-D5) | 1.81 | 0.83 | 195.1 | 148.0 |
| 4. | 5-Hydroxyindole-3-acetic acid (5-HIAA) | 1.83 | 21.6–32.7* | 190.0 | 145.9 |
| 5. | 4-Hydroxy-3-methoxyphenyl-D3-acetic-D2 acid (HVA-D5) | 2.11 | 0.83 | 186.1 | 127.0 |
| 6. | Homovanillic acid (HVA) | 2.14 | 12.9–18.9* | 181.0 | 121.9 |
Conditions
| Column | Raptor Biphenyl (cat.# 9309512) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dimensions: | 100 mm x 2.1 mm ID | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Particle Size: | 5 µm | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Pore Size: | 90 Å | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Guard Column: | Raptor Biphenyl guard column cartridge 5 mm, 2.1 mm ID, 5 µm (cat.# 930950252) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Temp.: | 30 °C | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Standard/Sample | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Diluent: | Water | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Inj. Vol.: | 5 µL | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Mobile Phase | |||||||||||||||||||||
| A: | 0.1% Formic acid, 5 mM ammonium formate in water | ||||||||||||||||||||
| B: | Methanol | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
| Detector | MS/MS |
|---|---|
| Ion Mode: | ESI- |
| Mode: | MRM |
| Instrument | UHPLC |
| Sample Preparation | The human urine sample is the Bio-Rad Lyphochek quantitative urine control, level 2. A 40 μL aliquot of urine was mixed with 360 μL of water and 10 μL of internal standard solution (33.3 μg/mL in methanol) in a Thomson 0.45 μm PVDF filter vial and injected for analysis after filtration. |