Content previously published in Petro Industry News
When using PLOT columns to analyze trace impurities in petroleum gases, such as propylene, ethylene, or 1,3-butadiene, sample handling capacity (loadability) is an important factor in obtaining accurate data. Phase overload results in peak tailing, which can be problematic when trace level impurities elute near the main component where they may be obscured by the larger peak. Peak tailing can be further exacerbated by residual activity on the adsorbent surface. Using a higher sample capacity column with an appropriate deactivation is a good strategy for reducing tailing and improving accurate quantification of low level polar impurities in volatile petroleum streams.
MAPD alumina PLOT columns are commonly used for these applications because the selectivity of alumina makes it very useful for separating C1-C5 hydrocarbons. Although selectivity is very good for these compounds, sample capacity is often poor, which limits the amount of sample that can be injected. Larger sample volumes can be desirable when less sensitive detectors (e.g. TCDs) are used or when trace levels of impurities, such as acetylene, propadiene, or methyl acetylene, must be detected in order to prevent damage to polymerization catalysts.
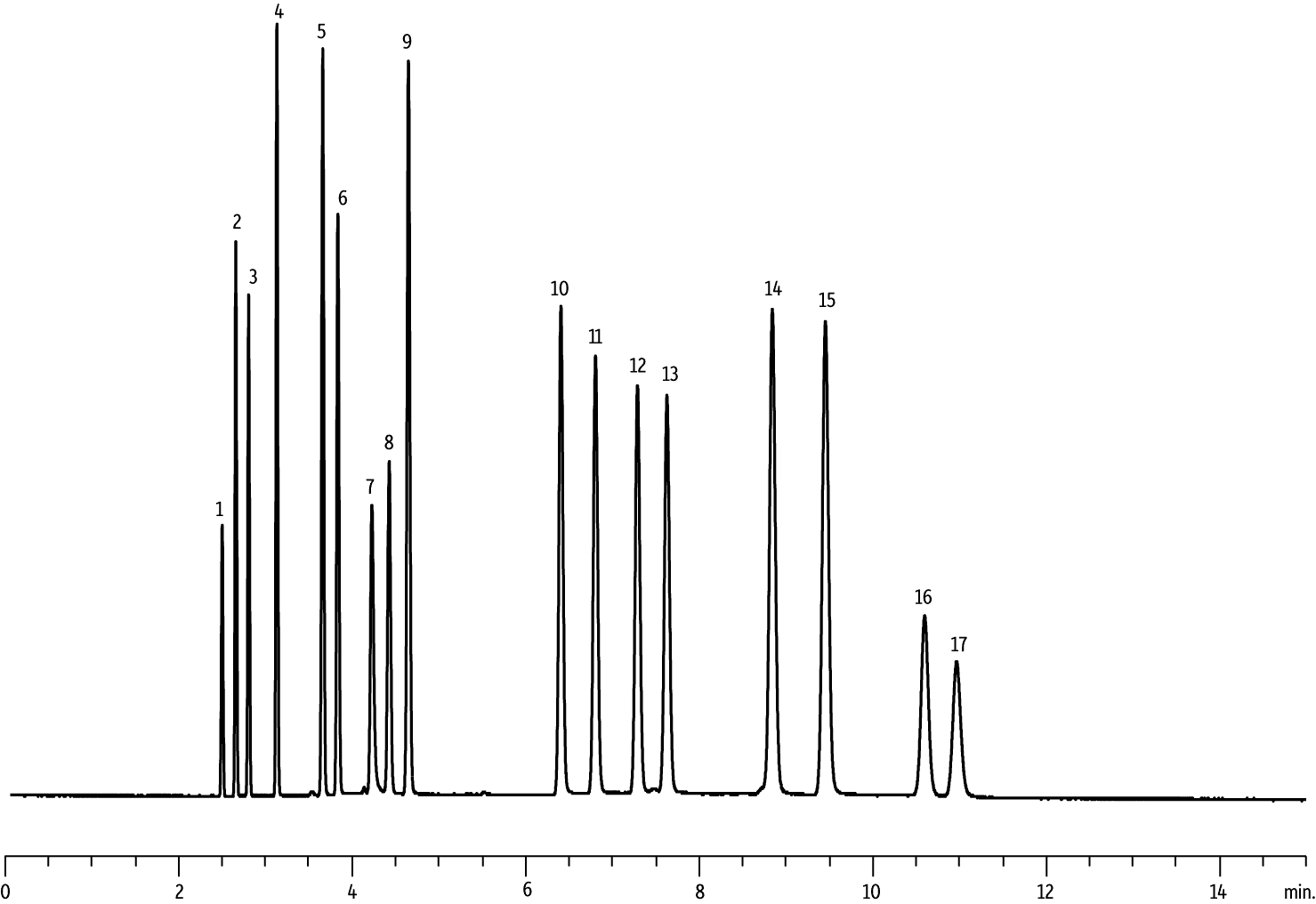
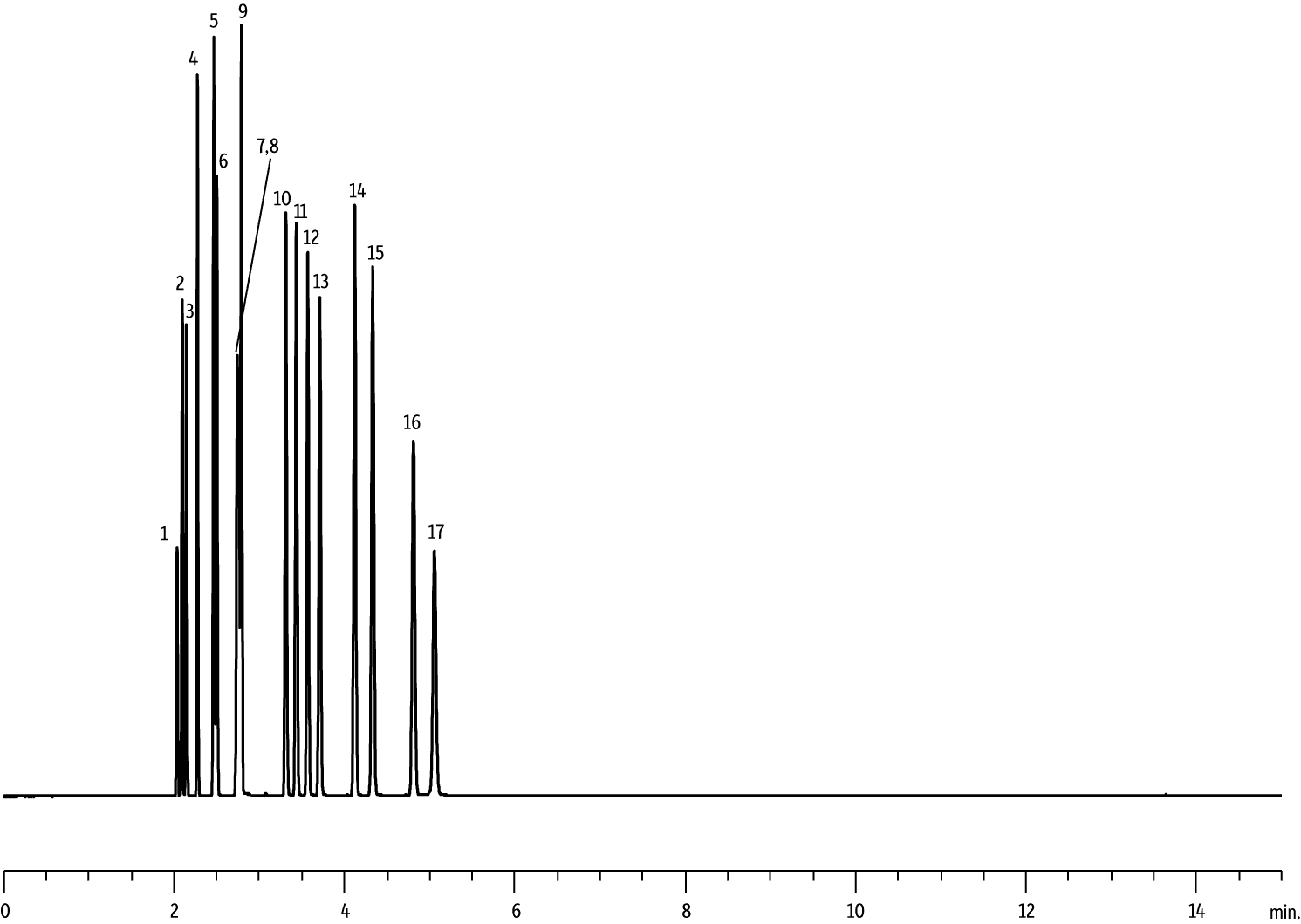
New Rt-Alumina BOND/MAPD columns have an improved deactivation, increased sample capacity, and greater absolute retention compared to other commercially available MAPD PLOT columns. As shown in a comparison of absolute retention times, all peaks are well resolved on the Rt-Alumina BOND/MAPD column and no coelutions are observed (Figure 1). Greater retention increases resolution, which reduces the likelihood of coelution and can lessen the impact of tailing. Absolute retention was compared using an isothermal oven temperature of 130 °C; however, several critical compounds were not resolved on the Select Al2O3 MAPD column at this temperature, so optimized conditions for each column were used for sample capacity evaluations.
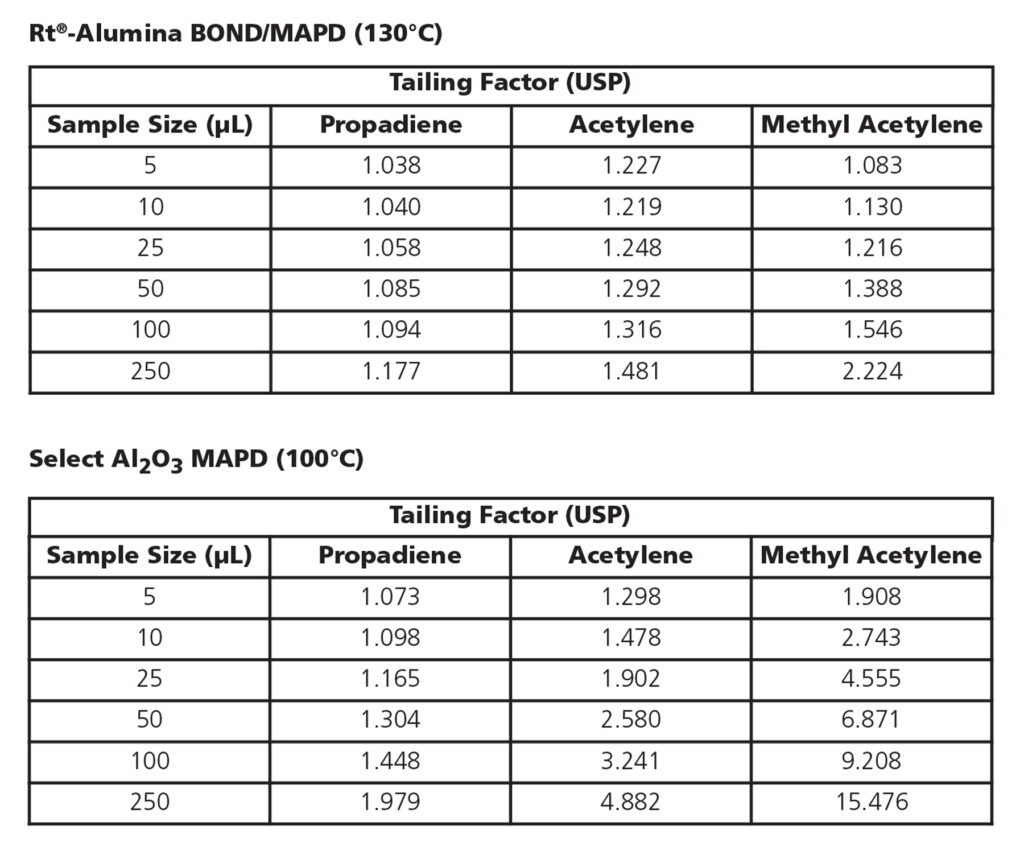
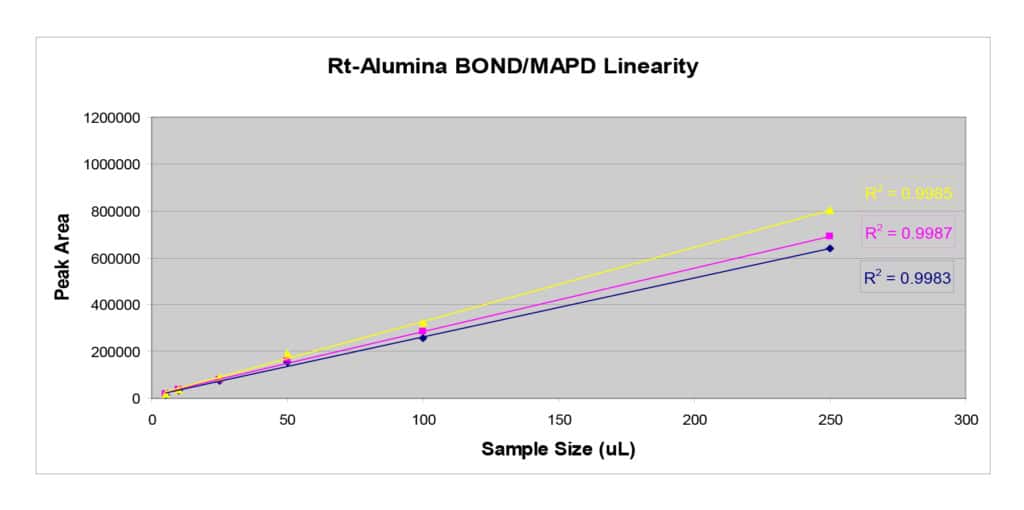
To assess sample capacity, each column was tested at the temperature shown on the manufacturer’s QA protocol in order to achieve comparable retention and adequate resolution. A range of sample volumes of a QA test mix were analyzed on each column using a 6-port sampling valve and 5 µL to 250 µL sample loops. Peak tailing was measured for the analytes that were most likely to exhibit tailing and be sensitive to poor sample capacity in actual impurity testing. As shown in Table I, much less peak tailing was observed on the Rt-Alumina BOND/MAPD column. Symmetrical peaks were obtained across a wide sample volume range, indicating that the column deactivation was highly effective and also that sample capacity was greater on the Rt-Alumina BOND/MAPD column. Linearity was also assessed, as shown in Figure 2, and excellent correlations were achieved for all target impurities across the test range.
When analyzing impurities, such as acetylene, propadiene, and methyl acetylene in petroleum gases, the sample handling capacity of the analytical column is an important consideration. Rt-Alumina BOND/MAPD columns offer higher sample capacity than other commercially available MAPD columns and are recommended for analyzing polar impurities in light hydrocarbon streams. Greater sample capacity improves data accuracy due to better peak symmetry and a wide linear range.
1A. Rt-Alumina BOND/MAPD
GC_PC1213
Peaks
| Peaks | |
|---|---|
| 1. | Methane |
| 2. | Ethane |
| 3. | Ethylene |
| 4. | Propane |
| 5. | Cyclopropane |
| 6. | Propylene |
| 7. | Acetylene |
| 8. | Propadiene |
| Peaks | |
|---|---|
| 9. | n-Butane |
| 10. | trans-2-Butene |
| 11. | 1-Butene |
| 12. | Isobutene |
| 13. | cis-2-Butene |
| 14. | Isopentane |
| 15. | n-Pentane |
| 16. | 1,3-Butadiene |
| 17. | Methyl acetylene |
Conditions
| Column | Rt-Alumina BOND/MAPD, 50 m, 0.53 mm ID, 10 µm (cat.# 19778) |
|---|---|
| Standard/Sample | DCG custom standard |
| Injection | |
| Inj. Vol.: | 5 µL split |
| Liner: | 2 mm single taper |
| Inj. Temp.: | 200 °C |
| Split Vent Flow Rate: | 80 mL/min. |
| Oven | |
| Oven Temp.: | 130 °C (hold 15 min) |
| Carrier Gas | He, constant pressure (4.4 psi, 30.3 kPa) |
| Temp.: | 130 °C |
| Detector | FID @ 200 °C |
|---|---|
| Instrument | HP5890 GC |
| Notes | Liner cat.# 20795 was used to produce this chromatogram, but it has since been discontinued. We recommend cat.# 20796 [or cat.# 23315] as an alternative. For assistance choosing a replacement for this application, contact Restek Technical Service or your local Restek representative. |
1B. Select Al2O3 MAPD
GC_PC1214
Peaks
| Peaks | |
|---|---|
| 1. | Methane |
| 2. | Ethane |
| 3. | Ethylene |
| 4. | Propane |
| 5. | Cyclopropane |
| 6. | Propylene |
| 7. | Acetylene |
| 8. | Propadiene |
| Peaks | |
|---|---|
| 9. | n-Butane |
| 10. | trans-2-Butene |
| 11. | 1-Butene |
| 12. | Isobutene |
| 13. | cis-2-Butene |
| 14. | Isopentane |
| 15. | n-Pentane |
| 16. | 1,3-Butadiene |
| 17. | Methyl acetylene |
Conditions
| Column | Varian Select Al2O3 MAPD (CP7432), 50 m, 0.53 mm ID, 10 µm |
|---|---|
| Standard/Sample | DCG Custom Standard |
| Injection | |
| Inj. Vol.: | 5 µL split |
| Liner: | 2 mm single gooseneck |
| Inj. Temp.: | 200 °C |
| Split Vent Flow Rate: | 80 mL/min. |
| Oven | |
| Oven Temp.: | 130 °C (hold 8 min) |
| Carrier Gas | He, constant pressure (4.4 psi, 30.3 kPa) |
| Temp.: | 130 °C |
| Detector | FID @ 200 °C |
|---|---|
| Instrument | HP5890 GC |
| Notes | GC liner cat.# 20795 was used to produce this chromatogram, but it has since been discontinued. For assistance choosing a liner for this application, contact Restek Technical Service or your local Restek representative. |