Save Time and Money with QuEChERS
- Free-flowing salts in slim packets make extraction a snap.
- Complete line of easy-to-use QuEChERS products, reference standards, and accessories.
- Follow up sample prep with a wide range of analytical columns for both LC and GC.

convenient slim packets fit perfectly into tubes to prevent spills
For years, the QuEChERS approach to sample preparation has been making the lives of food safety scientists easier. Gone are the days of time-consuming, solvent-intensive extraction techniques and multiple solid phase extraction cartridge cleanup steps! Research published by the U.S. Department of Agriculture Eastern Regional Research Center in Wyndmoor, PA, [1] introduced to the world QuEChERS—a method that is Quick, Easy, Cheap, Effective, Rugged, and Safe.
With QuEChERS, a homogenized sample simply undergoes a quick extraction step where the analytes are driven into an organic solvent by the partitioning power of a blend of salts. After extraction, the sample is cleaned up through the use of a dispersive solid phase extraction (dSPE) step that is also quick and easy to perform. This simple, two-stage process offers significant savings in time, materials, and effort, making QuEChERS sample preparation faster and easier than other approaches (Table I).
Since its introduction, the QuEChERS technique has evolved to accommodate an expanding list of pesticides in an increasingly diverse list of foodstuffs. At Restek, we offer Q-sep products to cover the four major approaches to QuEChERS along with a host of other items to help make your QuEChERS experience simple and successful. We carry a comprehensive line of sample prep supplies, reference standards, and LC and GC columns that will help make QuEChERS even easier whether you are new to the approach or developing a method for a new sample matrix. If you are frustrated with the time and expense of your current pesticide sample cleanup procedure, we suggest you try this simple, economical technique.
Table I: Prepare samples more quickly, easily, and cost effectively with QuEChERS.
| Mini-Luke or Modified Luke Method | QuEChERS | Savings with QuEChERS | |
| Estimated time to process 6 samples (min) | 120 | 30 | 4x faster |
| Solvent used (mL) | 60-90 | 10 | 6-9x less solvent |
| Chlorinated waste (mL) | 20-30 | 0 | Safer, cheaper, greener |
| Glassware/specialized equipment | capacity for 200 mL, quartz wool, funnel, water bath, or evaporator | None | Read |
Quick and Easy…
Prepare Samples for LC or GC Analysis in Two Simple Stages
QuEChERS is primarily a two-stage process, and you’ll select Q-sep products for both stages. Your method may have specific recommendations, but in case you’re not sure what will work, here are some considerations when making your selection.
Stage 1: Sample Extraction
Analytes of interest are extracted from the sample through the addition of an organic solvent and a blend of salts. The salts enhance extraction efficiency and allow the normally miscible organic solvent to separate from the water in the sample. The choice of which extraction technique to use is made principally by considering your analytes of interest. If you’re looking for compounds that aren’t pH sensitive, the original unbuffered method [1] will work great. However, if your analytes of interest are pH sensitive, you will want to select one of the buffered methods—notably, the official EN 15662 method [2], the mini-multiresidue approach [3], or the official AOAC 2007.01 method [4].
Restek’s Q-sep products for the two European approaches, the official EN 15662 method and the mini-multiresidue approach, are the same, so it becomes essentially a choice between a European-developed method and the AOAC method. Both are buffered to lower the pH to a range where most pesticides are stable, and the methods differ only in the specific buffering salts and their ratios. Either would be a good place to start for most analyses. There are a great many studies that highlight specific instances when one buffering technique may outperform another, so a little research into your particular area of study may yield practical suggestions on which extraction method to use.


Stage 2: Sample Cleanup
A subsample of the organic solvent extract from Stage 1 is cleaned up through the use of dSPE. Where the choice of the extraction product was driven largely by the analytes of interest, the choice of cleanup is based on the sample being tested. Restek Q-sep dSPE products are formulated with different sorbents in different ratios so that your dSPE choice can be tailored to the composition of your particular sample type (e.g., fatty, highly pigmented, etc.). Use Table III further below to learn what each sorbent removes and to help select the best dSPE product for your particular sample.

Effective…
QuEChERS dSPE Cleanup Assures Optimal Results for Pesticide Analysis
- Removes matrix interferences that obscure target analytes or cause ion suppression.
- Protects GC inlet, and LC and GC columns from contamination.
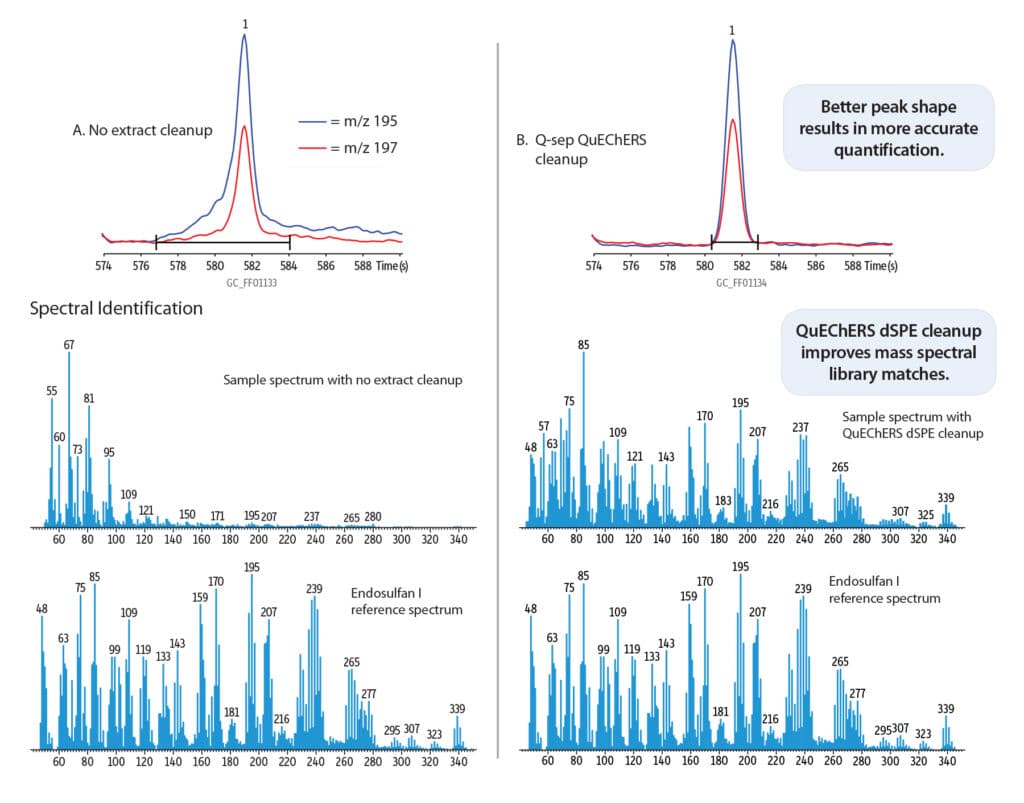
- Improves integration and mass spectral matches
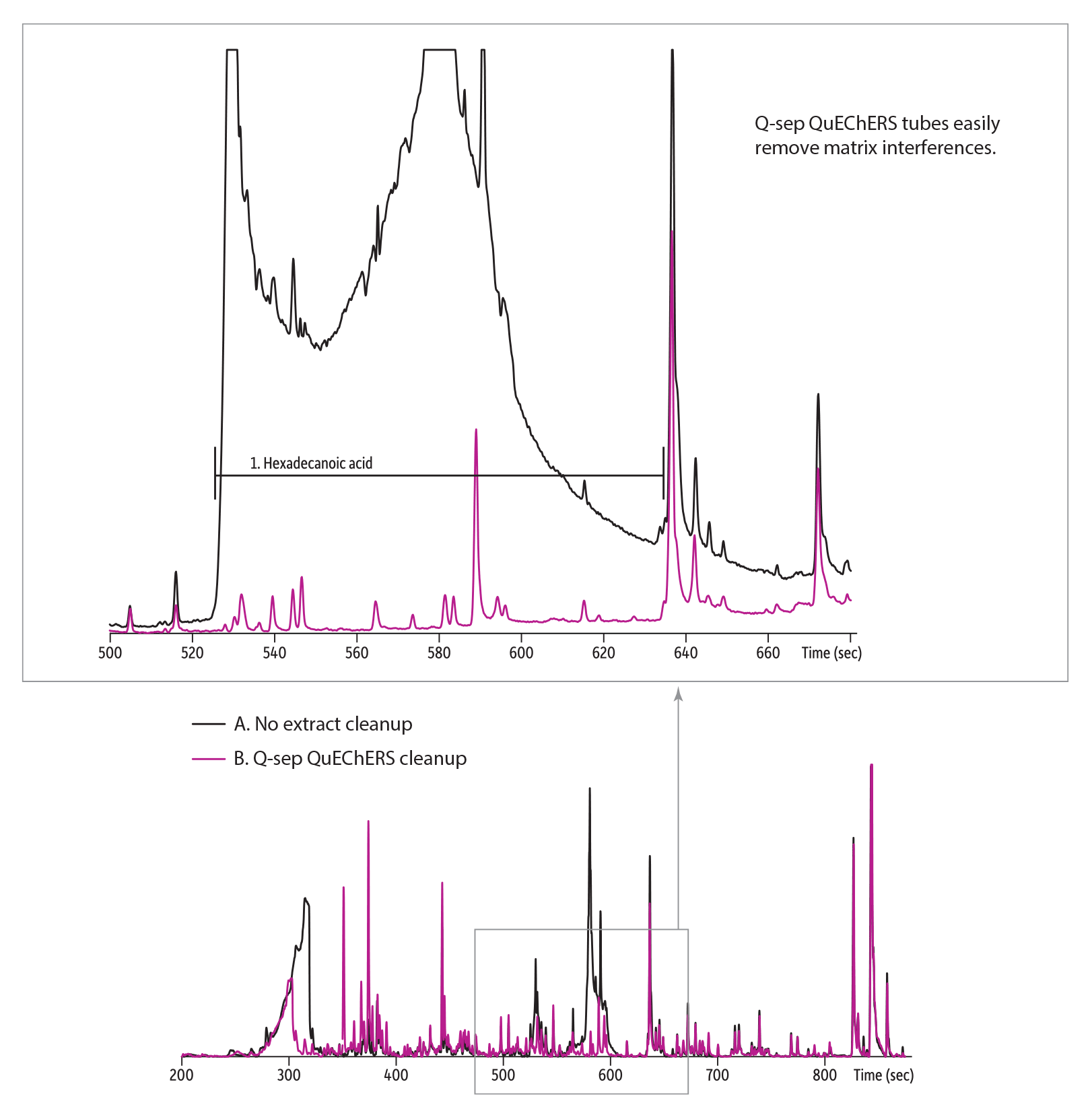
Without extract cleanup, hexadecanoic acid from the matrix obscures peaks for all the following pesticides.
(example XIC chromatogram = endosulfan I)
allethrin
buprofezin
cis-chlordane
trans-chlordane
chlorpyrifos
cyprodinil
dacthal
diphenamid
endosulfan I
endosulfan II
fenthion
metolachlor
myclobutanil
oxyfluorfen
pendimethalin
pentachlorothioanisole
pirimiphos methyl
triadimefon
triadimenol
GC_FF01125_1127
Conditions
| Column | Rxi-5Sil MS, 20 m, 0.18 mm ID, 0.18 µm (cat.# 43602) |
|---|---|
| Standard/Sample | Sweet potato spiked with pesticide mix and extracted with acetonitrile and Q-sep QuEChERS EN Method 15662 extraction salts |
| Injection | |
| Inj. Vol.: | 1.0 µL splitless (hold 1 min) |
| Liner: | Single taper (4 mm) w/deact. wool |
| Inj. Temp.: | 250 °C |
| Oven | |
| Oven Temp.: | 72.5 °C (hold 1 min) to 350 °C at 20 °C/min |
| Carrier Gas | He, constant flow |
| Flow Rate: | 1.2 mL/min |
| Detector | MS |
|---|---|
| Mode: | |
| Transfer Line Temp.: | 300 °C |
| Analyzer Type: | TOF |
| Ionization Mode: | EI |
| Acquisition Range: | 45-550 amu |
| Instrument | Agilent/HP6890 GC |
| Sample Preparation | A. Extract (without cleanup step) acidified with formic acid to pH 5. B. Extract with cleanup using Q-sep QuEChERS dSPE cleanup tube (cat.# 26124) acidified with formic acid to pH 5. |
| Notes | Liner cat.# 22405 was used to produce this chromatogram, but it has since been discontinued. We recommend cat.# 22406 [or cat.# 23303] as an alternative. For assistance choosing a replacement for this application, contact Restek Technical Service or your local Restek representative. – – – – – – m/z 60, 73, 87, 129, 256 plotted |
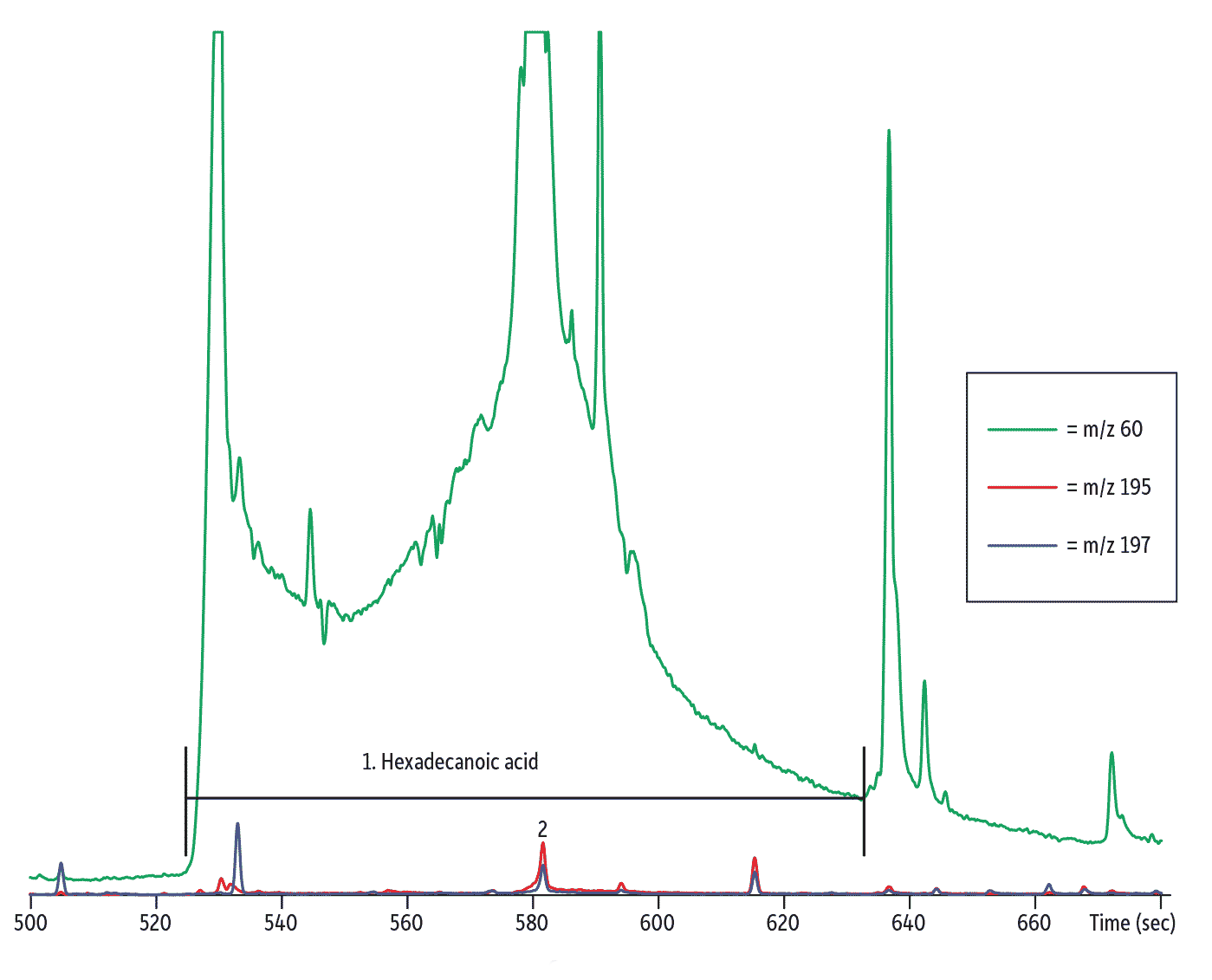
Without cleanup, matrix masks Endosulfan I.
GC_FF1222
Peaks
| Peaks | |
|---|---|
| 1. | Hexadecanoic acid |
| 2. | Endosulfan I |
Conditions
| Column | Rxi-5Sil MS, 20 m, 0.18 mm ID, 0.18 µm (cat.# 43602) |
|---|---|
| Standard/Sample | Sweet potato spiked with pesticide mix and extracted with acetonitrile and Q-sep QuEChERS extraction salts, then acidified with formic acid to pH 5. |
| Injection | |
| Inj. Vol.: | 1 µL splitless (hold 1 min) |
| Liner: | Gooseneck splitless (4 mm) w/deact. wool |
| Inj. Temp.: | 250 °C |
| Oven | |
| Oven Temp.: | 72.5 °C (hold 1 min) to 350 °C at 20 °C/min |
| Carrier Gas | He, constant flow |
| Flow Rate: | 1.2 mL/min |
| Detector | MS |
|---|---|
| Mode: | |
| Transfer Line Temp.: | 300 °C |
| Analyzer Type: | TOF |
| Ionization Mode: | EI |
| Acquisition Range: | 45 to 550 amu |
| Instrument | LECO Pegasus III GC-TOFMS |
| Notes | Liner cat.# 22405 was used to produce this chromatogram, but it has since been discontinued. We recommend cat.# 22406 [or cat.# 23303] as an alternative. For assistance choosing a replacement for this application, contact Restek Technical Service or your local Restek representative. – – – – – – m/z 60, 195, 197 shown |
QuEChERS dSPE cleanup improves quantification and identification.
Peak Integration (extracted ion chromatograms)
Optimize Analysis with Sorbent Choice
Choosing a QuEChERS dSPE Sorbent
Primary and secondary amine exchange material (PSA) is the base sorbent used for QuEChERS dSPE cleanup of fruit and vegetable extracts because it removes many organic acids and sugars that might act as instrumental interferences. In addition, C18 or graphitized carbon black (GCB) may be used to remove lipids or pigments, respectively. Choice of sorbent should be based on matrix composition and target analyte chemistry. Most methods make specific recommendations for acidic, basic, and planar pesticides, which may require additional considerations.
As seen in Table II, GCB can have a negative effect on the recoveries of certain pesticides that can assume planar shapes (e.g., chlorothalonil and thiabendazole). The work shown here was done with 50 mg GCB per mL extract, which emphasizes this effect. The EN 15662 QuEChERS method recommends less GCB, which improves recoveries of planar pesticides but still assures the removal of pigments that can degrade GC-MS performance. To simplify and speed up sample prep, Restek QuEChERS tubes are available in the sorbent combinations and amounts specified by EN 15662 and AOAC methods, as well as in other combinations that may provide better results for difficult matrices (Table III).
Table II: Select sorbents based on matrix and target analyte chemistry. (Percent recovery using C18 or GCB, relative to PSA alone).
| tR (min) | Pesticide | CAS Number | Action/Use | Classification | C18* | GCB** |
| 9.50 | Dichlorvos | 62-73-7 | insecticide | organophosphorus | 111 | 116 |
| 9.67 | Methamidophos | 10265-92-6 | insecticide | organophosphorus | 105 | 107 |
| 11.75 | Mevinphos | 7786-34-7 | insecticide | organophosphorus | 112 | 130 |
| 12.02 | o-phenylphenol | 90-43-7 | fungicide | unclassified | 106 | 97 |
| 12.14 | Acephate | 30560-19-1 | insecticide | organophosphorus | 128 | 147 |
| 13.89 | Omethoate | 1113-02-6 | insecticide | organophosphorus | 120 | 119 |
| 14.74 | Diazinon | 333-41-5 | insecticide | organophosphorus | 108 | 127 |
| 14.98 | Dimethoate | 60-51-5 | insecticide | organophosphorus | 124 | 151 |
| 15.69 | Chlorothalonil | 1897-45-6 | fungicide | organochlorine | 125 | 13 |
| 15.86 | Vinclozolin | 50471-44-8 | fungicide | organochlorine | 102 | 98 |
| 16.21 | Metalaxyl | 57837-19-1 | fungicide | organonitrogen | 105 | 117 |
| 16.28 | Carbaryl | 63-25-2 | insecticide | carbamate | 114 | 111 |
| 16.60 | Malathion | 121-75-5 | insecticide | organophosphorus | 124 | 160 |
| 16.67 | Dichlofluanid | 1085-98-9 | fungicide | organohalogen | 122 | 103 |
| 17.51 | Thiabendazole | 148-79-8 | fungicide | organonitrogen | 88 | 14 |
| 17.70 | Captan | 133-06-2 | fungicide | organochlorine | 88 | 91 |
| 17.76 | Folpet | 133-07-3 | fungicide | organochlorine | 108 | 63 |
| 18.23 | Imazalil | 35554-44-0 | fungicide | organonitrogen | 115 | 95 |
| 18.39 | Endrin | 72-20-8 | insecticide | organochlorine | 104 | 101 |
| 18.62 | Myclobutanil | 88671-89-0 | fungicide | organonitrogen | 119 | 114 |
| 19.07 | 4,4-DDT | 50-29-3 | insecticide | organochlorine | 102 | 95 |
| 19.22 | Fenhexamid | 126833-17-8 | fungicide | organochlorine | 118 | 77 |
| 19.40 | Propargite 1 | 2312-35-8 | acaricide | organosulfur | 110 | 95 |
| 19.43 | Propargite 2 | 2312-35-8 | acaricide | organosulfur | 121 | 114 |
| 19.75 | Bifenthrin | 82657-04-3 | insecticide | pyrethroid | 106 | 81 |
| 20.04 | Dicofol | 115-32-2 | acaricide | organochlorine | 98 | 54 |
| 20.05 | Iprodione | 36734-19-7 | fungicide | organonitrogen | 118 | 90 |
| 20.21 | Fenpropathrin | 39515-41-8 | insecticide | pyrethroid | 113 | 96 |
| 21.32 | cis-Permethrin | 52645-53-1 | insecticide | pyrethroid | 106 | 65 |
| 21.47 | trans-Permethrin | 51877-74-8 | insecticide | pyrethroid | 109 | 71 |
| 23.74 | Deltamethrin | 52918-63-5 | insecticide | pyrethroid | 97 | 52 |
*50 mg PSA, 50 mg C18, **50 mg PSA, 50 mg GCB

Strawberry extracts were spiked at 200 ng/mL with pesticides and subjected to dSPE with PSA only. Results were used to generate single-point calibration curves. Spiked extracts were then subjected to additional dSPE sorbents (either C18 or GCB). Results are shown as percent recoveries relative to PSA alone.
Table III: Restek Q-sep dSPE products are formulated with different sorbents in different ratios so that your dSPE choice can be tailored to the composition of your particular sample type (e.g., fatty, highly pigmented, etc.)
| Method | Sorbent Mass (mg) | Product Information | ||||
| MgSO₄ | PSA* | C18-EC | GCB** | Vial Volume (mL) | Cat.# | |
| Removes | ||||||
| Excess water | Sugars, fatty acids, organic acids, anthocyanine pigments | Lipids, nonpolar interferences | Pigments, sterols, nonpolar interferences | |||
| Sample Type: General fruits and vegetables Example: Celery, head lettuce, cucumber, melon |
||||||
| AOAC 2007.01 | 150 | 50 | – | – | 2 | 26124 |
| Original unbuffered, EN 15662, mini-multiresidue | 150 | 25 | – | – | 2 | 26215 |
| AOAC 2007.01 | 1200 | 400 | – | – | 15 | 26220 |
| Original unbuffered, EN 15662 | 900 | 150 | – | – | 15 | 26223 |
| Sample Type: Foodstuffs with fats and waxes Example: Cereals, avocado, nuts, seeds, and dairy |
||||||
| Mini-multiresidue | 150 | 25 | 25 | – | 2 | 26216 |
| – | 150 | – | 50 | – | 2 | 26242 |
| AOAC 2007.01 | 150 | 50 | 50 | – | 2 | 26125 |
| AOAC 2007.01 | 1200 | 400 | 400 | – | 15 | 26221 |
| – | 1200 | – | 400 | – | 15 | 26244 |
| – | 900 | 150 | 150 | – | 15 | 26226 |
| Sample Type: Pigmented fruits and vegetables Example: Strawberries, sweet potatoes, tomatoes |
||||||
| Mini-multiresidue, EN 15662 | 150 | 25 | – | 2.5 | 2 | 26217 |
| AOAC 2007.01 | 150 | 50 | – | 50 | 2 | 26123 |
| AOAC 2007.01 | 1200 | 400 | 400 | 400 | 15 | 26222 |
| EN 15662 | 900 | 150 | – | 15 | 15 | 26224 |
| Sample Type: Highly pigmented fruits and vegetables Example: Red peppers, spinach, blueberries |
||||||
| Mini-multiresidue, EN 15662 | 150 | 25 | – | 7.5 | 2 | 26218 |
| AOAC 2007.01 | 150 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 2 | 26219 |
| EN 15662 | 900 | 150 | – | 45 | 15 | 26225 |
| – | 900 | 300 | – | 150 | 15 | 26126 |
| Sample Type: General purpose Example: Wide range of commodities, including fatty and pigmented fruits and vegetables |
||||||
| – | 150 | 50 | 50 | 7.5 | 2 | 26243 |
| – | 900 | 300 | 300 | 45 | 15 | 26245 |
Note: No entry in the Method column refers to dSPE formulations not specifically included in one of the cited references. These products can be used to accommodate the various needs of specific matrices not directly met by the cited references.
*PSA = primary secondary amine exchange material
**GCB = graphitized carbon black
Try QuEChERS risk-free today!
Call Restek or your local Restek representative to request a free sample pack of Q-sep QuEChERS tubes.
References
Restek is not able to provide copies of these documents.
- M. Anastassiades, S.J. Lehotay, D. Stajnbaher, F.J. Schenck, Fast and easy multiresidue method employing acetonitrile extraction/partitioning and “dispersive solid-phase extraction” for the determination of pesticide residues in produce. J. AOAC Int. 86 (2003) 412-431. http://pubag.nal.usda.gov/pubag/downloadPDF.xhtml?id=555&content=PDF
- EN 15662, Foods of Plant Origin—Determination of Pesticide Residues Using GC-MS and/or LC-MS/MS Following Acetonitrile Extraction/Partitioning and Clean-up by Dispersive SPE—QuEChERS method, 2008.
- QuEChERS-A Mini-Multiresidue Method for the Analysis of Pesticide Residues in Low-Fat Products, 2004. http://quechers.cvua-stuttgart.de/pdf/reality.pdf
- AOAC Official Method 2007.01, Pesticide Residues in Foods by Acetonitrile Extraction and Partitioning with Magnesium Sulfate, 2007.


