Fast, Optimized GC Purge-and-Trap Analysis of Volatiles for Soil and Water Methods
- Save set-up time—we’ve optimized volatiles analysis for you!
- Fit-for-purpose Rtx-VMS column separates early eluting gases and critical VOCs, ensuring rugged, accurate volatiles analysis.
- Precisely formulated CRMs ensure accurate quantitation and are backed by Restek’s ISO accreditation and rigorous documentation.
Volatile organic compounds (VOCs) pose human health risks and can enter the environment and water supplies through a number of avenues, such as the improper disposal of industrial chemicals (e.g., chlorinated solvents) or the leaking of fuel components from underground storage tanks. Monitoring programs often utilize GC purge-and-trap analysis of volatiles in soil and water samples in order to track VOC contamination. The first fused silica columns used for this analysis were based on diphenyl/dimethyl polysiloxane stationary phases. However, resolution of gases has always been problematic with these columns. In support of labs conducting purge-and-trap analysis of volatiles, Restek designed the Rtx-VMS column specifically to optimize the separation of commonly analyzed VOCs of environmental concern. The Rtx-VMS column features a stationary phase that is selective for VOCs, a film thickness sufficient to retain and resolve the low boiling volatiles, and enough thermal stability to elute the high boiling VOCs.
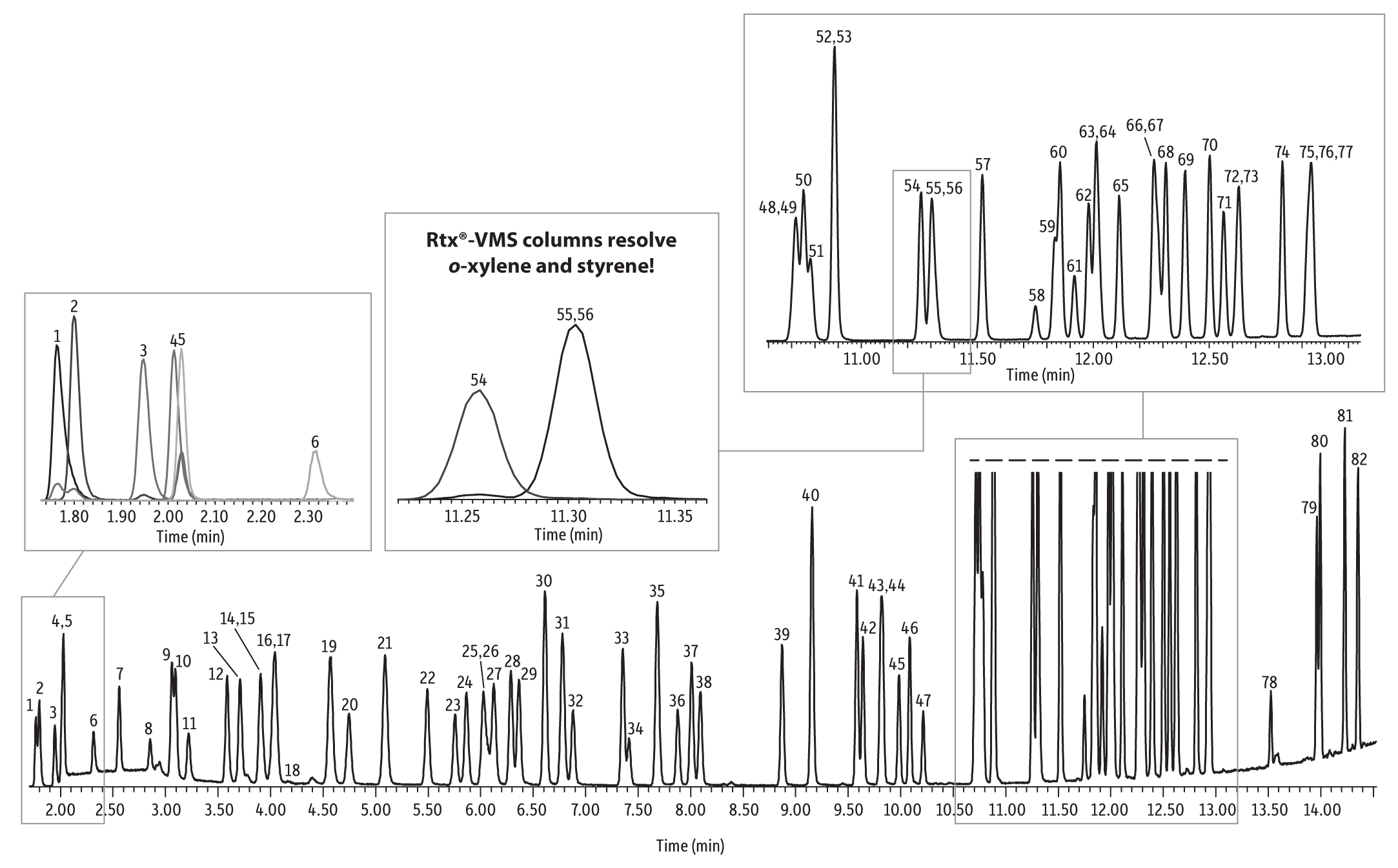
Since the Rtx-VMS column has been optimized for volatiles analysis, it provides excellent resolution of critical VOCs, which ensures more accurate quantification in fast analysis times. As shown in the chromatograms below, data quality and lab productivity can be increased using an Rtx-VMS column paired with Restek certified reference materials (CRMs). In the first example, excellent resolution of the 82 drinking water contaminants listed in EPA Method 524.3 was obtained—including o-xylene and styrene, which often coelute on other columns. Labs that include the seven volatiles listed in the Unregulated Contaminant Monitoring Rule 3 (UCMR3) in their drinking water analyses will benefit greatly from this application and these products. Having all VOCs packaged in only three ampuls with CRM documentation simplifies the task of calibration. In addition, separating and detecting volatiles using the Rtx-VMS column delivers the best quality data for purge-and-trap analysis of volatiles in drinking water.
The second chromatogram shown below demonstrates the performance of the Rtx-VMS in separating a longer list of volatiles, specifically the 102 VOCs listed in EPA Method 8260. While EPA Method 524.3 was written for purgeable organic compounds in water samples, EPA Method 8260 can be used for purge-and-trap analysis of volatiles in a much more diverse array of sample types (soil, water, solid waste, etc.) In this example, good chromatographic results are again obtained for both early- and late-eluting volatiles, but the separation of oxygenates is particularly noteworthy. Oxygenates are added to gasolines to enhance fuel performance, and they are target compounds in leaking underground storage tank monitoring. Purge-and-trap GC-MS analysis with a highly selective Rtx-VMS column is recommended for this method because key oxygenates—such as methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE) and tert-butyl alcohol (TBA)—coelute on other GC columns and they also share the ions used for identification. In addition to separating these components in the reference standards shown below, the Rtx-VMS column can resolve MTBE and TBA as well as additional oxygenates from other target compounds and potentially interfering matrix components in gasoline. To see the separation and identification of 5 ppb oxygenates in a gasoline sample, read our application note.
As shown in the chromatograms below, Restek’s combination of CRMs and the Rtx-VMS column are highly effective tools that are optimized for GC purge-and-trap analysis of volatiles. The unique Rtx-VMS column phase offers the best separation of critical compound pairs on the market. In addition, Restek CRMs are comprehensive, manufactured and QC-tested in our ISO-accredited labs, and come complete with all necessary documentation to make your job easier.
GC_EV1297
Peaks
Conditions
| Column | Rtx-VMS, 30 m, 0.25 mm ID, 1.40 µm (cat.# 19915) |
|---|---|
| Standard/Sample | |
| 524.3 internal standard/surrogate mix (cat.# 30017) | |
| 524.3 gas calibration mix (cat.# 30014) | |
| 524.3 VOA MegaMix standard (cat.# 30013) | |
| Diluent: | RO water |
| Conc.: | 5 ng/mL (5 mL sample) |
| Injection | purge and trap split (split ratio 30:1) |
| Liner: | Premium 1.0mm ID straight inlet liner (cat.# 23333) |
| Inj. Temp.: | 200 °C |
| Purge and Trap | |
| Instrument: | EST Encon Evolution |
| Trap Type: | Vocarb 3000 |
| Purge: | 11 min, flow 40 mL/min |
| Dry Purge: | 1 min, flow 50 mL/min |
| Desorb: | 1 min @ 260 °C, flow 30.9 mL/min |
| Bake: | 8 min @ 265 °C |
| Interface Connection: | injection port |
| Transfer Line Temp.: | 150 °C |
| Oven | |
| Oven Temp.: | 45 °C (hold 4.5 min) to 100 °C at 12 °C/min to 240 °C at 25 °C/min (hold 1.32 min) |
| Carrier Gas | He, constant flow |
| Flow Rate: | 0.9 mL/min |
| Detector | MS | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mode: | Scan | ||||||||||||
| Scan Program: | |||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||
| Transfer Line Temp.: | 240 °C | ||||||||||||
| Analyzer Type: | Quadrupole | ||||||||||||
| Source Temp.: | 230 °C | ||||||||||||
| Quad Temp.: | 150 °C | ||||||||||||
| Electron Energy: | 70 eV | ||||||||||||
| Solvent Delay Time: | 1.5 min | ||||||||||||
| Tune Type: | BFB | ||||||||||||
| Ionization Mode: | EI | ||||||||||||
| Instrument | Agilent 7890A GC & 5975C MSD | ||||||||||||
| Acknowledgement | EST Analytical provided the Centurion robotic autosampler and Encon Evolution P&T concentrator. | ||||||||||||


